Details of the Target
General Information of Target
| Target ID | LDTP00521 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Name | Period circadian protein homolog 2 (PER2) | |||||
| Gene Name | PER2 | |||||
| Gene ID | 8864 | |||||
| Synonyms |
KIAA0347; Period circadian protein homolog 2; hPER2; Circadian clock protein PERIOD 2 |
|||||
| 3D Structure | ||||||
| Sequence |
MNGYAEFPPSPSNPTKEPVEPQPSQVPLQEDVDMSSGSSGHETNENCSTGRDSQGSDCDD
SGKELGMLVEPPDARQSPDTFSLMMAKSEHNPSTSGCSSDQSSKVDTHKELIKTLKELKV HLPADKKAKGKASTLATLKYALRSVKQVKANEEYYQLLMSSEGHPCGADVPSYTVEEMES VTSEHIVKNADMFAVAVSLVSGKILYISDQVASIFHCKRDAFSDAKFVEFLAPHDVGVFH SFTSPYKLPLWSMCSGADSFTQECMEEKSFFCRVSVRKSHENEIRYHPFRMTPYLVKVRD QQGAESQLCCLLLAERVHSGYEAPRIPPEKRIFTTTHTPNCLFQDVDERAVPLLGYLPQD LIETPVLVQLHPSDRPLMLAIHKKILQSGGQPFDYSPIRFRARNGEYITLDTSWSSFINP WSRKISFIIGRHKVRVGPLNEDVFAAHPCTEEKALHPSIQELTEQIHRLLLQPVPHSGSS GYGSLGSNGSHEHLMSQTSSSDSNGHEDSRRRRAEICKNGNKTKNRSHYSHESGEQKKKS VTEMQTNPPAEKKAVPAMEKDSLGVSFPEELACKNQPTCSYQQISCLDSVIRYLESCNEA ATLKRKCEFPANVPALRSSDKRKATVSPGPHAGEAEPPSRVNSRTGVGTHLTSLALPGKA ESVASLTSQCSYSSTIVHVGDKKPQPELEMVEDAASGPESLDCLAGPALACGLSQEKEPF KKLGLTKEVLAAHTQKEEQSFLQKFKEIRKLSIFQSHCHYYLQERSKGQPSERTAPGLRN TSGIDSPWKKTGKNRKLKSKRVKPRDSSESTGSGGPVSARPPLVGLNATAWSPSDTSQSS CPAVPFPAPVPAAYSLPVFPAPGTVAAPPAPPHASFTVPAVPVDLQHQFAVQPPPFPAPL APVMAFMLPSYSFPSGTPNLPQAFFPSQPQFPSHPTLTSEMASASQPEFPSRTSIPRQPC ACPATRATPPSAMGRASPPLFQSRSSSPLQLNLLQLEEAPEGGTGAMGTTGATETAAVGA DCKPGTSRDQQPKAPLTRDEPSDTQNSDALSTSSGLLNLLLNEDLCSASGSAASESLGSG SLGCDASPSGAGSSDTSHTSKYFGSIDSSENNHKAKMNTGMEESEHFIKCVLQDPIWLLM ADADSSVMMTYQLPSRNLEAVLKEDREKLKLLQKLQPRFTESQKQELREVHQWMQTGGLP AAIDVAECVYCENKEKGNICIPYEEDIPSLGLSEVSDTKEDENGSPLNHRIEEQT |
|||||
| Target Bioclass |
Other
|
|||||
| Subcellular location |
Nucleus; Nucleus, nucleolus
|
|||||
| Function |
Transcriptional repressor which forms a core component of the circadian clock. The circadian clock, an internal time-keeping system, regulates various physiological processes through the generation of approximately 24 hour circadian rhythms in gene expression, which are translated into rhythms in metabolism and behavior. It is derived from the Latin roots 'circa' (about) and 'diem' (day) and acts as an important regulator of a wide array of physiological functions including metabolism, sleep, body temperature, blood pressure, endocrine, immune, cardiovascular, and renal function. Consists of two major components: the central clock, residing in the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) of the brain, and the peripheral clocks that are present in nearly every tissue and organ system. Both the central and peripheral clocks can be reset by environmental cues, also known as Zeitgebers (German for 'timegivers'). The predominant Zeitgeber for the central clock is light, which is sensed by retina and signals directly to the SCN. The central clock entrains the peripheral clocks through neuronal and hormonal signals, body temperature and feeding-related cues, aligning all clocks with the external light/dark cycle. Circadian rhythms allow an organism to achieve temporal homeostasis with its environment at the molecular level by regulating gene expression to create a peak of protein expression once every 24 hours to control when a particular physiological process is most active with respect to the solar day. Transcription and translation of core clock components (CLOCK, NPAS2, BMAL1, BMAL2, PER1, PER2, PER3, CRY1 and CRY2) plays a critical role in rhythm generation, whereas delays imposed by post-translational modifications (PTMs) are important for determining the period (tau) of the rhythms (tau refers to the period of a rhythm and is the length, in time, of one complete cycle). A diurnal rhythm is synchronized with the day/night cycle, while the ultradian and infradian rhythms have a period shorter and longer than 24 hours, respectively. Disruptions in the circadian rhythms contribute to the pathology of cardiovascular diseases, cancer, metabolic syndrome and aging. A transcription/translation feedback loop (TTFL) forms the core of the molecular circadian clock mechanism. Transcription factors, CLOCK or NPAS2 and BMAL1 or BMAL2, form the positive limb of the feedback loop, act in the form of a heterodimer and activate the transcription of core clock genes and clock-controlled genes (involved in key metabolic processes), harboring E-box elements (5'-CACGTG-3') within their promoters. The core clock genes: PER1/2/3 and CRY1/2 which are transcriptional repressors form the negative limb of the feedback loop and interact with the CLOCK|NPAS2-BMAL1|BMAL2 heterodimer inhibiting its activity and thereby negatively regulating their own expression. This heterodimer also activates nuclear receptors NR1D1/2 and RORA/B/G, which form a second feedback loop and which activate and repress BMAL1 transcription, respectively. PER1 and PER2 proteins transport CRY1 and CRY2 into the nucleus with appropriate circadian timing, but also contribute directly to repression of clock-controlled target genes through interaction with several classes of RNA-binding proteins, helicases and others transcriptional repressors. PER appears to regulate circadian control of transcription by at least three different modes. First, interacts directly with the CLOCK-BMAL1 at the tail end of the nascent transcript peak to recruit complexes containing the SIN3-HDAC that remodel chromatin to repress transcription. Second, brings H3K9 methyltransferases such as SUV39H1 and SUV39H2 to the E-box elements of the circadian target genes, like PER2 itself or PER1. The recruitment of each repressive modifier to the DNA seems to be very precisely temporally orchestrated by the large PER complex, the deacetylases acting before than the methyltransferases. Additionally, large PER complexes are also recruited to the target genes 3' termination site through interactions with RNA-binding proteins and helicases that may play a role in transcription termination to regulate transcription independently of CLOCK-BMAL1 interactions. Recruitment of large PER complexes to the elongating polymerase at PER and CRY termination sites inhibited SETX action, impeding RNA polymerase II release and thereby repressing transcriptional reinitiation. May propagate clock information to metabolic pathways via the interaction with nuclear receptors. Coactivator of PPARA and corepressor of NR1D1, binds rhythmically at the promoter of nuclear receptors target genes like BMAL1 or G6PC1. Directly and specifically represses PPARG proadipogenic activity by blocking PPARG recruitment to target promoters and thereby inhibiting transcriptional activation. Required for fatty acid and lipid metabolism, is involved as well in the regulation of circulating insulin levels. Plays an important role in the maintenance of cardiovascular functions through the regulation of NO and vasodilatatory prostaglandins production in aortas. Controls circadian glutamate uptake in synaptic vesicles through the regulation of VGLUT1 expression. May also be involved in the regulation of inflammatory processes. Represses the CLOCK-BMAL1 induced transcription of BHLHE40/DEC1 and ATF4. Negatively regulates the formation of the TIMELESS-CRY1 complex by competing with TIMELESS for binding to CRY1.
|
|||||
| Uniprot ID | ||||||
| Ensemble ID | ||||||
| HGNC ID | ||||||
| ChEMBL ID | ||||||
Target Site Mutations in Different Cell Lines
Probe(s) Labeling This Target
ABPP Probe
| Probe name | Structure | Binding Site(Ratio) | Interaction ID | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
DBIA Probe Info |
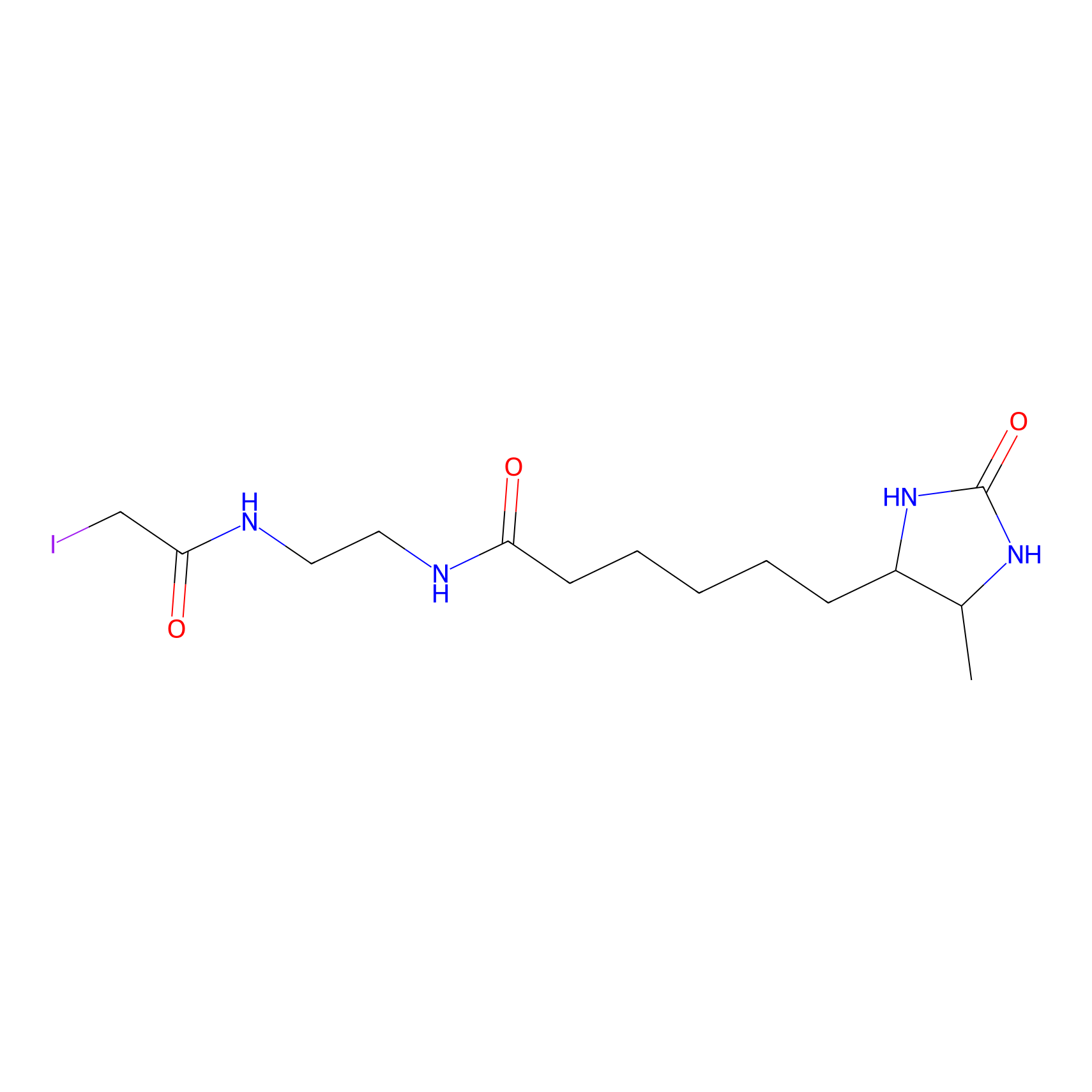 |
C579(1.26); C586(1.26) | LDD0078 | [1] | |
|
NAIA_5 Probe Info |
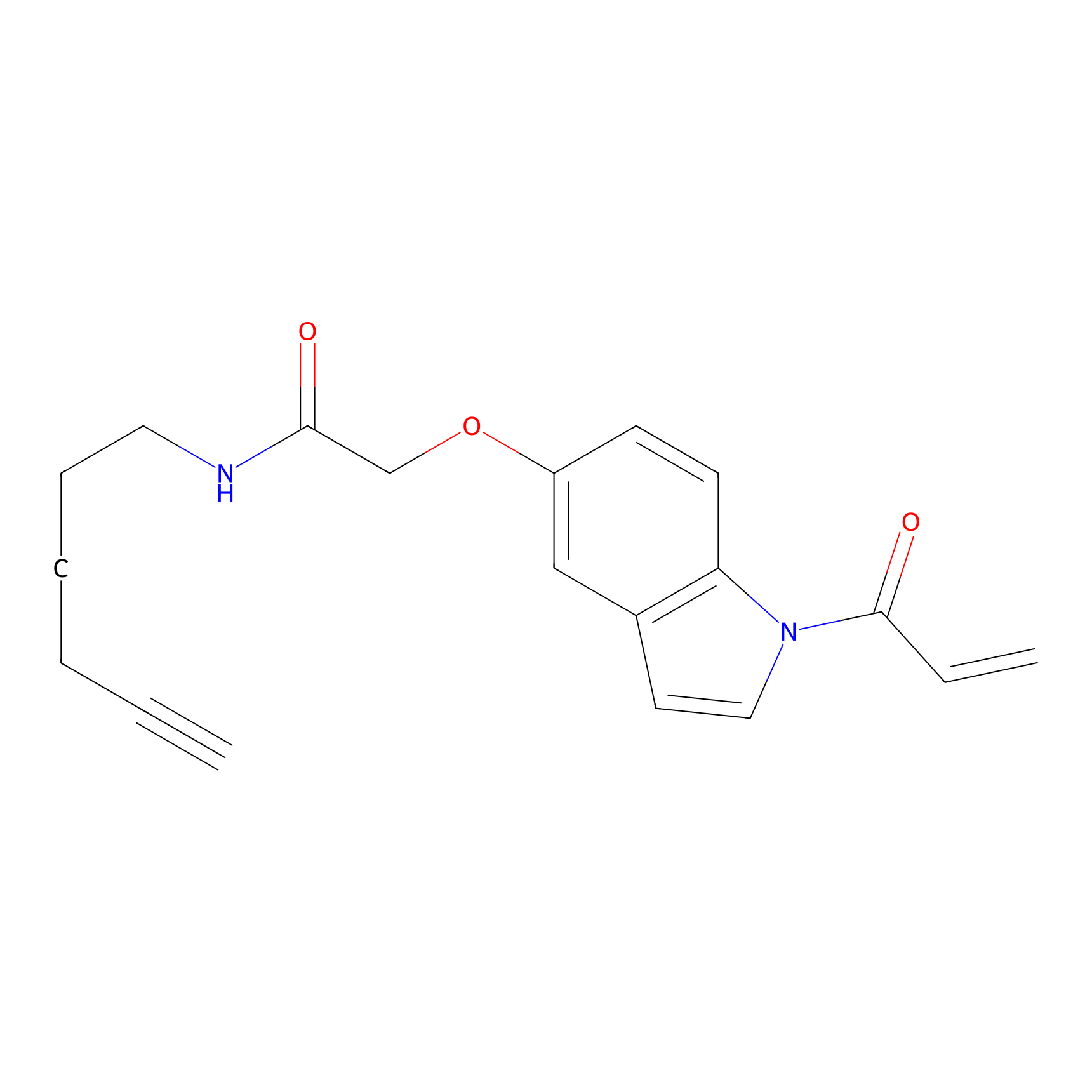 |
N.A. | LDD2225 | [2] | |
|
IPM Probe Info |
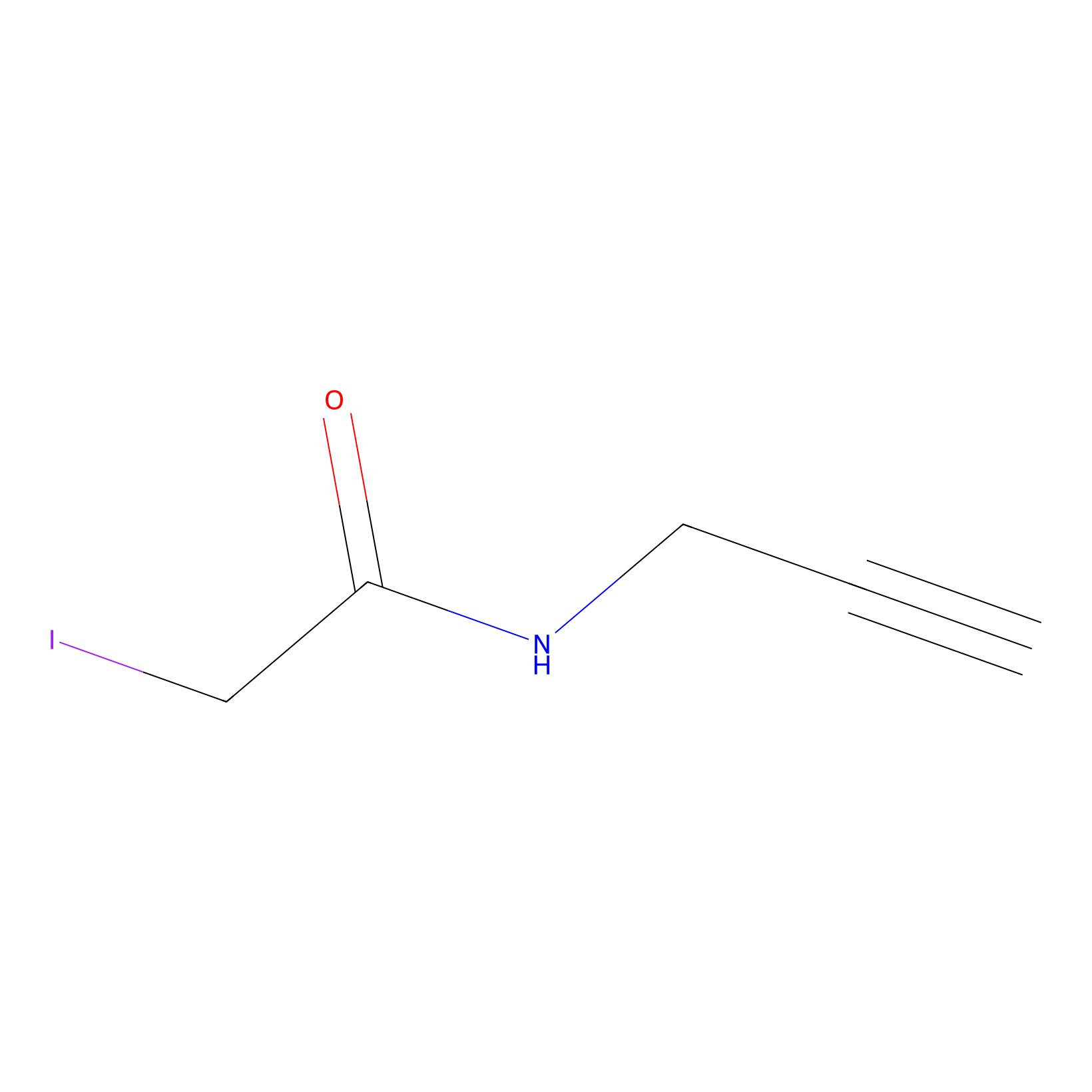 |
N.A. | LDD2156 | [3] | |
|
YN-1 Probe Info |
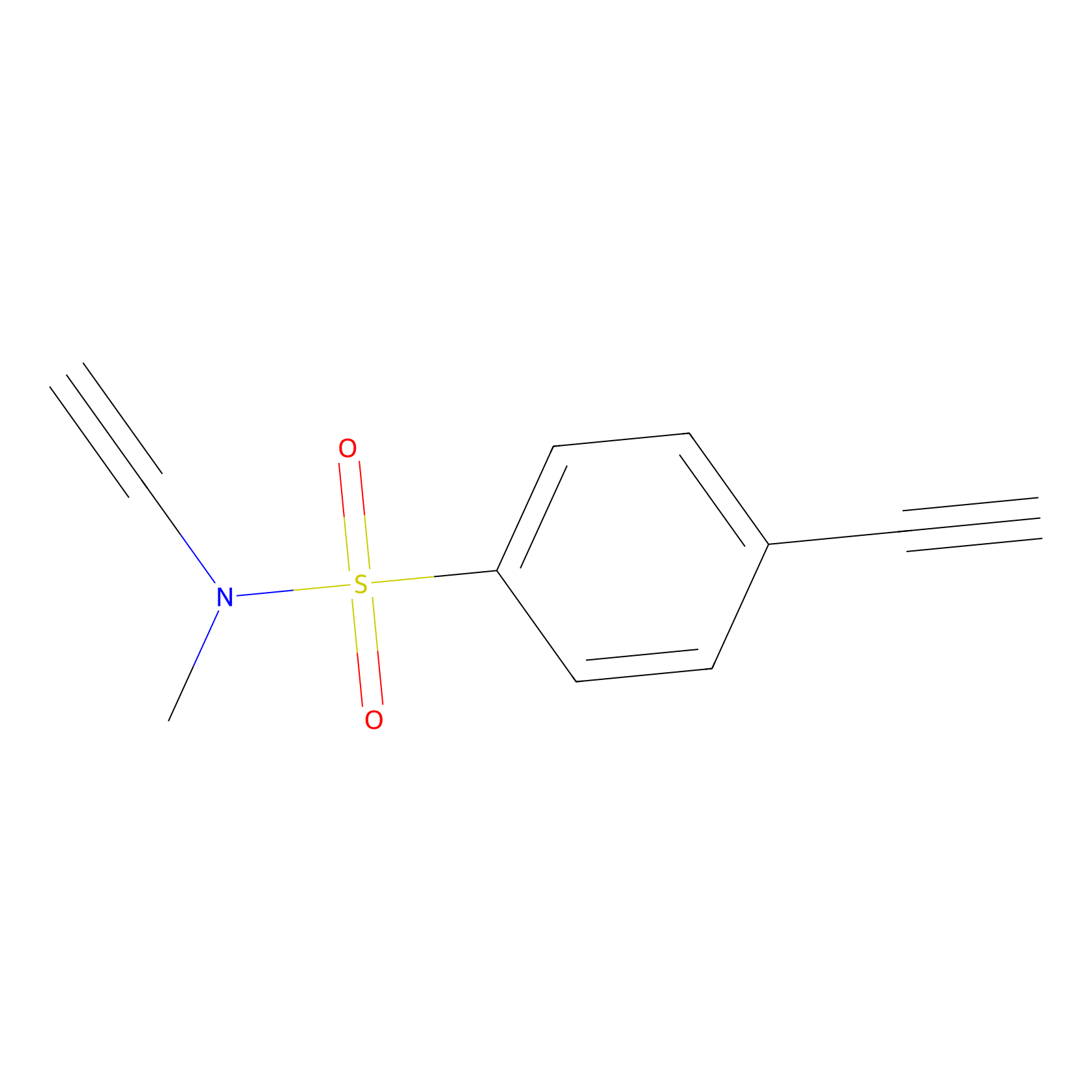 |
D300(0.00); E315(0.00) | LDD0447 | [4] | |
Competitor(s) Related to This Target
| Competitor ID | Name | Cell line | Binding Site(Ratio) | Interaction ID | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LDCM0214 | AC1 | HCT 116 | C579(0.67); C586(0.67) | LDD0531 | [1] |
| LDCM0216 | AC100 | HCT 116 | C579(0.88); C586(0.88) | LDD0533 | [1] |
| LDCM0217 | AC101 | HCT 116 | C579(1.03); C586(1.03) | LDD0534 | [1] |
| LDCM0218 | AC102 | HCT 116 | C579(0.81); C586(0.81) | LDD0535 | [1] |
| LDCM0219 | AC103 | HCT 116 | C579(1.17); C586(1.17) | LDD0536 | [1] |
| LDCM0220 | AC104 | HCT 116 | C579(1.10); C586(1.10) | LDD0537 | [1] |
| LDCM0221 | AC105 | HCT 116 | C579(1.35); C586(1.35) | LDD0538 | [1] |
| LDCM0222 | AC106 | HCT 116 | C579(1.06); C586(1.06) | LDD0539 | [1] |
| LDCM0223 | AC107 | HCT 116 | C579(1.35); C586(1.35) | LDD0540 | [1] |
| LDCM0224 | AC108 | HCT 116 | C579(0.92); C586(0.92) | LDD0541 | [1] |
| LDCM0225 | AC109 | HCT 116 | C579(0.76); C586(0.76) | LDD0542 | [1] |
| LDCM0227 | AC110 | HCT 116 | C579(0.77); C586(0.77) | LDD0544 | [1] |
| LDCM0228 | AC111 | HCT 116 | C579(0.91); C586(0.91) | LDD0545 | [1] |
| LDCM0229 | AC112 | HCT 116 | C579(1.20); C586(1.20) | LDD0546 | [1] |
| LDCM0263 | AC143 | HCT 116 | C579(0.78); C586(0.78) | LDD0580 | [1] |
| LDCM0264 | AC144 | HCT 116 | C579(0.76); C586(0.86) | LDD0581 | [1] |
| LDCM0265 | AC145 | HCT 116 | C586(0.87); C579(0.89) | LDD0582 | [1] |
| LDCM0266 | AC146 | HCT 116 | C579(0.69); C586(0.74) | LDD0583 | [1] |
| LDCM0267 | AC147 | HCT 116 | C579(0.81); C586(0.82) | LDD0584 | [1] |
| LDCM0268 | AC148 | HCT 116 | C579(0.57); C586(0.79) | LDD0585 | [1] |
| LDCM0269 | AC149 | HCT 116 | C579(0.89); C586(1.24) | LDD0586 | [1] |
| LDCM0271 | AC150 | HCT 116 | C579(0.65); C586(0.78) | LDD0588 | [1] |
| LDCM0272 | AC151 | HCT 116 | C579(0.88); C586(0.88) | LDD0589 | [1] |
| LDCM0273 | AC152 | HCT 116 | C586(0.77); C579(0.89) | LDD0590 | [1] |
| LDCM0274 | AC153 | HCT 116 | C579(0.65); C586(1.25) | LDD0591 | [1] |
| LDCM0621 | AC154 | HCT 116 | C579(0.74); C586(0.75) | LDD2158 | [1] |
| LDCM0622 | AC155 | HCT 116 | C579(0.65); C586(0.84) | LDD2159 | [1] |
| LDCM0623 | AC156 | HCT 116 | C579(0.72); C586(0.94) | LDD2160 | [1] |
| LDCM0624 | AC157 | HCT 116 | C579(0.80); C586(1.02) | LDD2161 | [1] |
| LDCM0279 | AC2 | HCT 116 | C579(0.55); C586(0.55) | LDD0596 | [1] |
| LDCM0290 | AC3 | HCT 116 | C579(0.75); C586(0.75) | LDD0607 | [1] |
| LDCM0301 | AC4 | HCT 116 | C579(0.73); C586(0.73) | LDD0618 | [1] |
| LDCM0312 | AC5 | HCT 116 | C579(0.64); C586(0.64) | LDD0629 | [1] |
| LDCM0349 | AC83 | HCT 116 | C579(1.42); C586(1.42) | LDD0666 | [1] |
| LDCM0350 | AC84 | HCT 116 | C579(1.78); C586(1.78) | LDD0667 | [1] |
| LDCM0351 | AC85 | HCT 116 | C579(1.40); C586(1.40) | LDD0668 | [1] |
| LDCM0352 | AC86 | HCT 116 | C579(2.11); C586(2.11) | LDD0669 | [1] |
| LDCM0353 | AC87 | HCT 116 | C579(3.21); C586(3.21) | LDD0670 | [1] |
| LDCM0354 | AC88 | HCT 116 | C579(2.30); C586(2.30) | LDD0671 | [1] |
| LDCM0355 | AC89 | HCT 116 | C579(2.22); C586(2.22) | LDD0672 | [1] |
| LDCM0357 | AC90 | HCT 116 | C579(1.51); C586(1.51) | LDD0674 | [1] |
| LDCM0358 | AC91 | HCT 116 | C579(1.74); C586(1.74) | LDD0675 | [1] |
| LDCM0359 | AC92 | HCT 116 | C579(2.29); C586(2.29) | LDD0676 | [1] |
| LDCM0360 | AC93 | HCT 116 | C579(1.91); C586(1.91) | LDD0677 | [1] |
| LDCM0361 | AC94 | HCT 116 | C579(1.66); C586(1.66) | LDD0678 | [1] |
| LDCM0362 | AC95 | HCT 116 | C579(2.50); C586(2.50) | LDD0679 | [1] |
| LDCM0363 | AC96 | HCT 116 | C579(3.42); C586(3.42) | LDD0680 | [1] |
| LDCM0364 | AC97 | HCT 116 | C579(2.59); C586(2.59) | LDD0681 | [1] |
| LDCM0365 | AC98 | HCT 116 | C579(1.65); C586(1.65) | LDD0682 | [1] |
| LDCM0366 | AC99 | HCT 116 | C579(0.70); C586(0.70) | LDD0683 | [1] |
| LDCM0020 | ARS-1620 | HCC44 | C579(1.26); C586(1.26) | LDD0078 | [1] |
| LDCM0632 | CL-Sc | Hep-G2 | C97(1.54) | LDD2227 | [2] |
| LDCM0367 | CL1 | HCT 116 | C579(1.27); C586(1.27) | LDD0684 | [1] |
| LDCM0368 | CL10 | HCT 116 | C579(1.23); C586(1.23) | LDD0685 | [1] |
| LDCM0369 | CL100 | HCT 116 | C579(0.79); C586(0.79) | LDD0686 | [1] |
| LDCM0379 | CL11 | HCT 116 | C579(1.28); C586(1.28) | LDD0696 | [1] |
| LDCM0390 | CL12 | HCT 116 | C579(0.84); C586(0.84) | LDD0707 | [1] |
| LDCM0400 | CL13 | HCT 116 | C579(1.06); C586(1.06) | LDD0717 | [1] |
| LDCM0401 | CL14 | HCT 116 | C579(1.33); C586(1.33) | LDD0718 | [1] |
| LDCM0402 | CL15 | HCT 116 | C579(1.23); C586(1.23) | LDD0719 | [1] |
| LDCM0407 | CL2 | HCT 116 | C579(1.25); C586(1.25) | LDD0724 | [1] |
| LDCM0418 | CL3 | HCT 116 | C579(1.26); C586(1.26) | LDD0735 | [1] |
| LDCM0429 | CL4 | HCT 116 | C579(0.98); C586(0.98) | LDD0746 | [1] |
| LDCM0440 | CL5 | HCT 116 | C579(1.22); C586(1.22) | LDD0757 | [1] |
| LDCM0451 | CL6 | HCT 116 | C579(1.24); C586(1.24) | LDD0768 | [1] |
| LDCM0462 | CL7 | HCT 116 | C579(0.98); C586(0.98) | LDD0779 | [1] |
| LDCM0469 | CL76 | HCT 116 | C579(1.18); C586(1.18) | LDD0786 | [1] |
| LDCM0470 | CL77 | HCT 116 | C579(1.42); C586(1.42) | LDD0787 | [1] |
| LDCM0471 | CL78 | HCT 116 | C579(2.00); C586(2.00) | LDD0788 | [1] |
| LDCM0472 | CL79 | HCT 116 | C579(1.24); C586(1.24) | LDD0789 | [1] |
| LDCM0473 | CL8 | HCT 116 | C579(0.89); C586(0.89) | LDD0790 | [1] |
| LDCM0474 | CL80 | HCT 116 | C579(1.18); C586(1.18) | LDD0791 | [1] |
| LDCM0475 | CL81 | HCT 116 | C579(1.25); C586(1.25) | LDD0792 | [1] |
| LDCM0476 | CL82 | HCT 116 | C579(1.39); C586(1.39) | LDD0793 | [1] |
| LDCM0477 | CL83 | HCT 116 | C579(1.36); C586(1.36) | LDD0794 | [1] |
| LDCM0478 | CL84 | HCT 116 | C579(1.20); C586(1.20) | LDD0795 | [1] |
| LDCM0479 | CL85 | HCT 116 | C579(1.14); C586(1.14) | LDD0796 | [1] |
| LDCM0480 | CL86 | HCT 116 | C579(1.14); C586(1.14) | LDD0797 | [1] |
| LDCM0481 | CL87 | HCT 116 | C579(1.16); C586(1.16) | LDD0798 | [1] |
| LDCM0482 | CL88 | HCT 116 | C579(1.20); C586(1.20) | LDD0799 | [1] |
| LDCM0483 | CL89 | HCT 116 | C579(1.44); C586(1.44) | LDD0800 | [1] |
| LDCM0484 | CL9 | HCT 116 | C579(1.15); C586(1.15) | LDD0801 | [1] |
| LDCM0485 | CL90 | HCT 116 | C579(1.96); C586(1.96) | LDD0802 | [1] |
| LDCM0486 | CL91 | HCT 116 | C579(0.60); C586(0.60) | LDD0803 | [1] |
| LDCM0487 | CL92 | HCT 116 | C579(0.67); C586(0.67) | LDD0804 | [1] |
| LDCM0488 | CL93 | HCT 116 | C579(0.58); C586(0.58) | LDD0805 | [1] |
| LDCM0489 | CL94 | HCT 116 | C579(0.59); C586(0.59) | LDD0806 | [1] |
| LDCM0490 | CL95 | HCT 116 | C579(0.74); C586(0.74) | LDD0807 | [1] |
| LDCM0491 | CL96 | HCT 116 | C579(0.68); C586(0.68) | LDD0808 | [1] |
| LDCM0492 | CL97 | HCT 116 | C579(0.75); C586(0.75) | LDD0809 | [1] |
| LDCM0493 | CL98 | HCT 116 | C579(0.61); C586(0.61) | LDD0810 | [1] |
| LDCM0494 | CL99 | HCT 116 | C579(0.69); C586(0.69) | LDD0811 | [1] |
| LDCM0022 | KB02 | HCC15 | C97(1.27) | LDD2340 | [5] |
| LDCM0023 | KB03 | HCC15 | C97(1.28) | LDD2757 | [5] |
| LDCM0024 | KB05 | NCI-H1155 | C97(1.38) | LDD3342 | [5] |
| LDCM0021 | THZ1 | HCT 116 | C579(1.16); C586(1.16) | LDD2173 | [1] |
The Interaction Atlas With This Target
The Protein(s) Related To This Target
Enzyme
Other
References
