Details of the Target
General Information of Target
| Target ID | LDTP11435 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Name | Charged multivesicular body protein 4a (CHMP4A) | |||||
| Gene Name | CHMP4A | |||||
| Gene ID | 29082 | |||||
| Synonyms |
C14orf123; SHAX2; Charged multivesicular body protein 4a; Chromatin-modifying protein 4a; CHMP4a; SNF7 homolog associated with Alix-2; SNF7-1; hSnf-1; Vacuolar protein sorting-associated protein 32-1; Vps32-1; hVps32-1
|
|||||
| 3D Structure | ||||||
| Sequence |
MGCDGGTIPKRHELVKGPKKVEKVDKDAELVAQWNYCTLSQEILRRPIVACELGRLYNKD
AVIEFLLDKSAEKALGKAASHIKSIKNVTELKLSDNPAWEGDKGNTKGDKHDDLQRARFI CPVVGLEMNGRHRFCFLRCCGCVFSERALKEIKAEVCHTCGAAFQEDDVIMLNGTKEDVD VLKTRMEERRLRAKLEKKTKKPKAAESVSKPDVSEEAPGPSKVKTGKPEEASLDSREKKT NLAPKSTAMNESSSGKAGKPPCGATKRSIADSEESEAYKSLFTTHSSAKRSKEESAHWVT HTSYCF |
|||||
| Target Bioclass |
Other
|
|||||
| Family |
SNF7 family
|
|||||
| Subcellular location |
Cytoplasmic vesicle membrane
|
|||||
| Function |
Probable core component of the endosomal sorting required for transport complex III (ESCRT-III) which is involved in multivesicular bodies (MVBs) formation and sorting of endosomal cargo proteins into MVBs. MVBs contain intraluminal vesicles (ILVs) that are generated by invagination and scission from the limiting membrane of the endosome and mostly are delivered to lysosomes enabling degradation of membrane proteins, such as stimulated growth factor receptors, lysosomal enzymes and lipids. The MVB pathway appears to require the sequential function of ESCRT-O, -I,-II and -III complexes. ESCRT-III proteins mostly dissociate from the invaginating membrane before the ILV is released. The ESCRT machinery also functions in topologically equivalent membrane fission events, such as the terminal stages of cytokinesis and the budding of enveloped viruses (HIV-1 and other lentiviruses). ESCRT-III proteins are believed to mediate the necessary vesicle extrusion and/or membrane fission activities, possibly in conjunction with the AAA ATPase VPS4. When overexpressed, membrane-assembled circular arrays of CHMP4A filaments can promote or stabilize negative curvature and outward budding. Via its interaction with PDCD6IP involved in HIV-1 p6- and p9-dependent virus release. CHMP4A/B/C are required for the exosomal release of SDCBP, CD63 and syndecan.
|
|||||
| Uniprot ID | ||||||
| Ensemble ID | ||||||
| HGNC ID | ||||||
Probe(s) Labeling This Target
ABPP Probe
| Probe name | Structure | Binding Site(Ratio) | Interaction ID | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
C-Sul Probe Info |
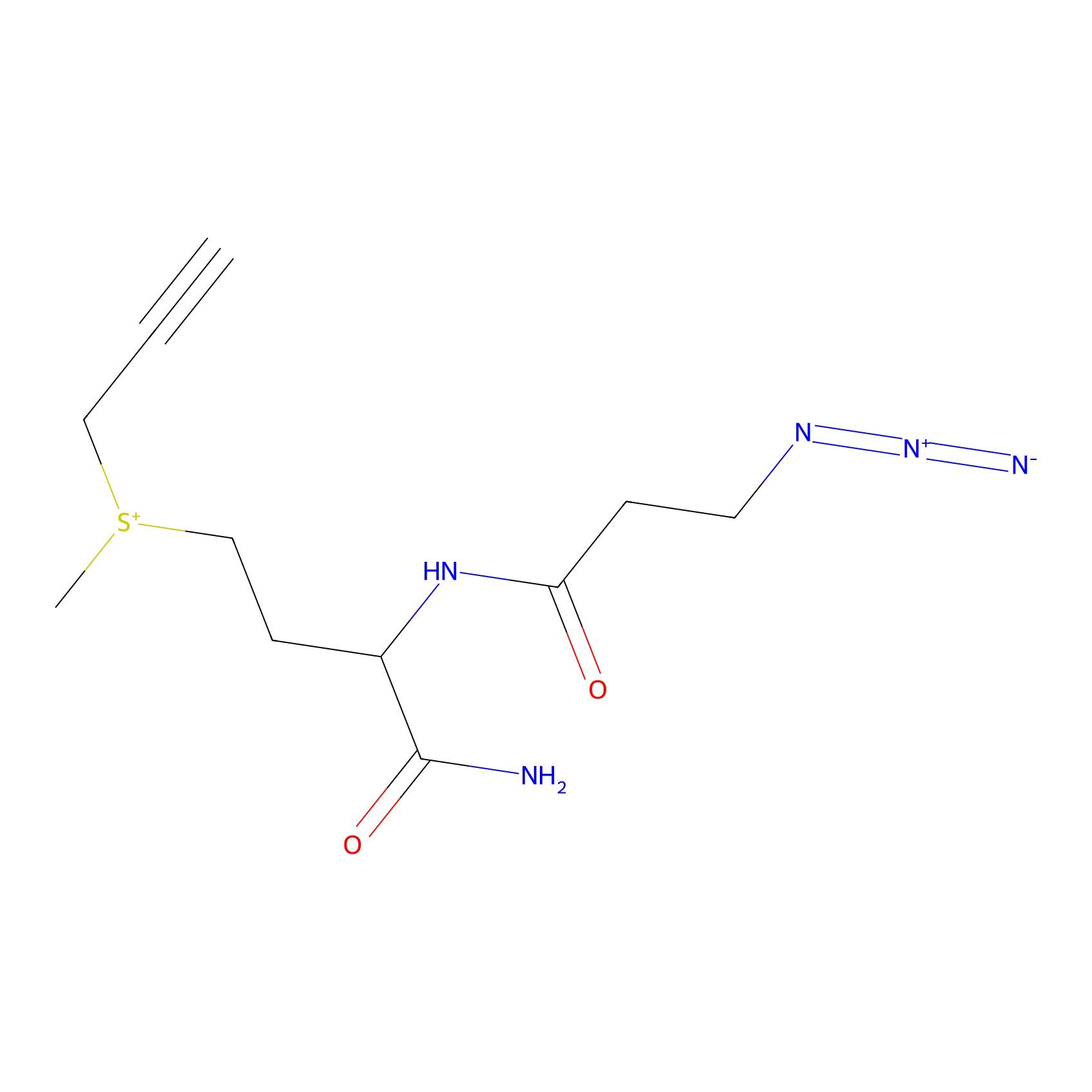 |
5.99 | LDD0066 | [1] | |
|
STPyne Probe Info |
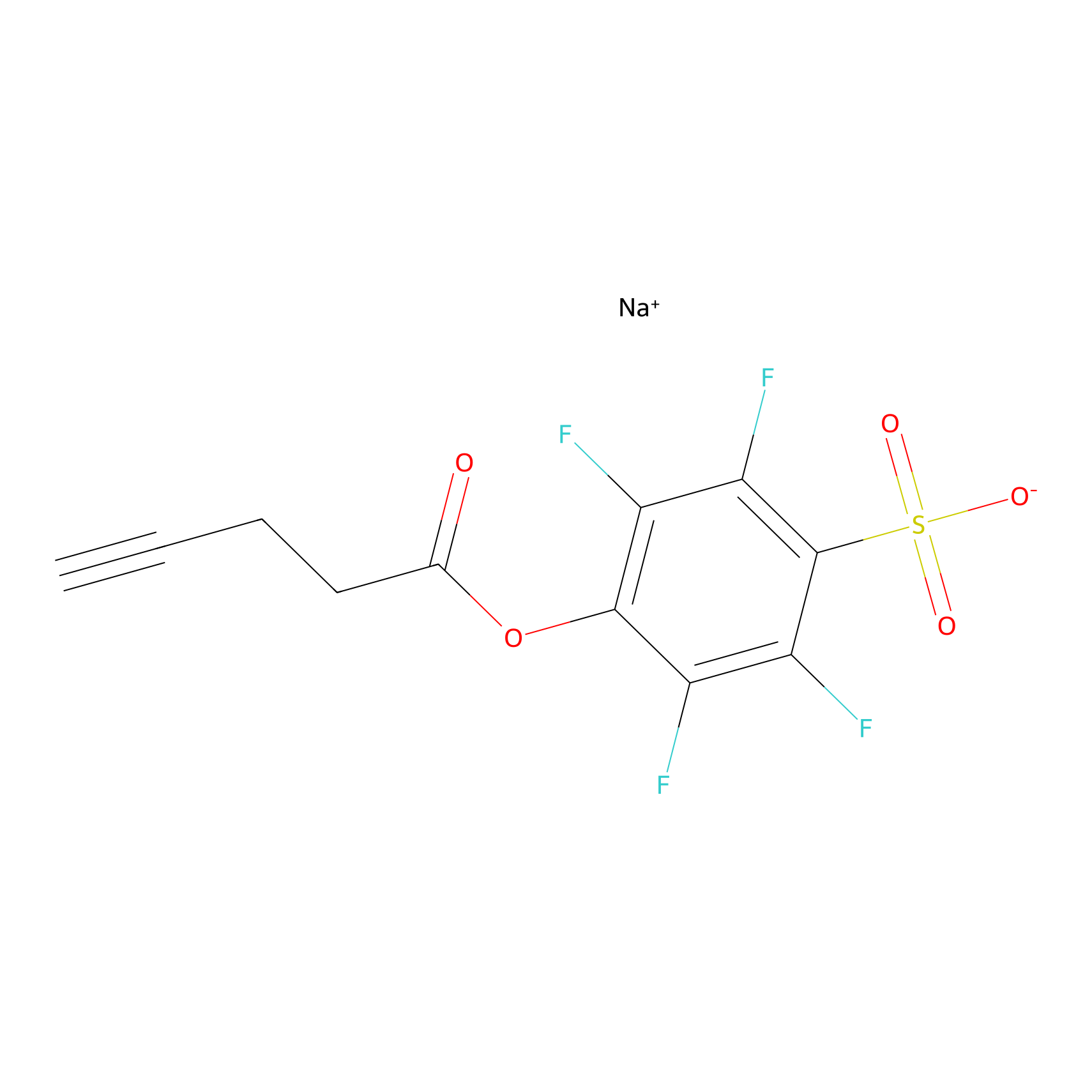 |
K25(7.05); K36(10.00) | LDD0277 | [2] | |
|
Probe 1 Probe Info |
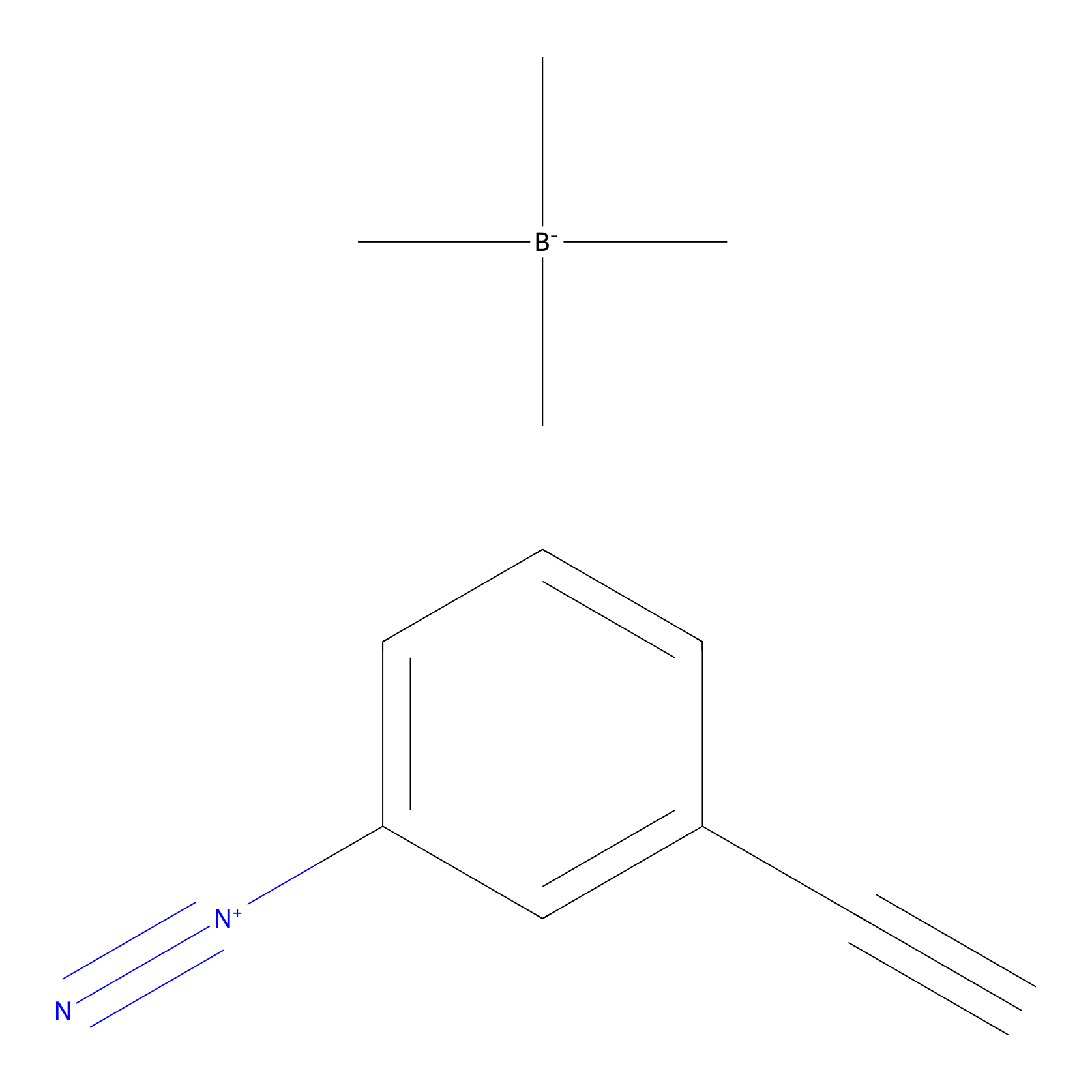 |
Y117(25.22) | LDD3495 | [3] | |
|
5E-2FA Probe Info |
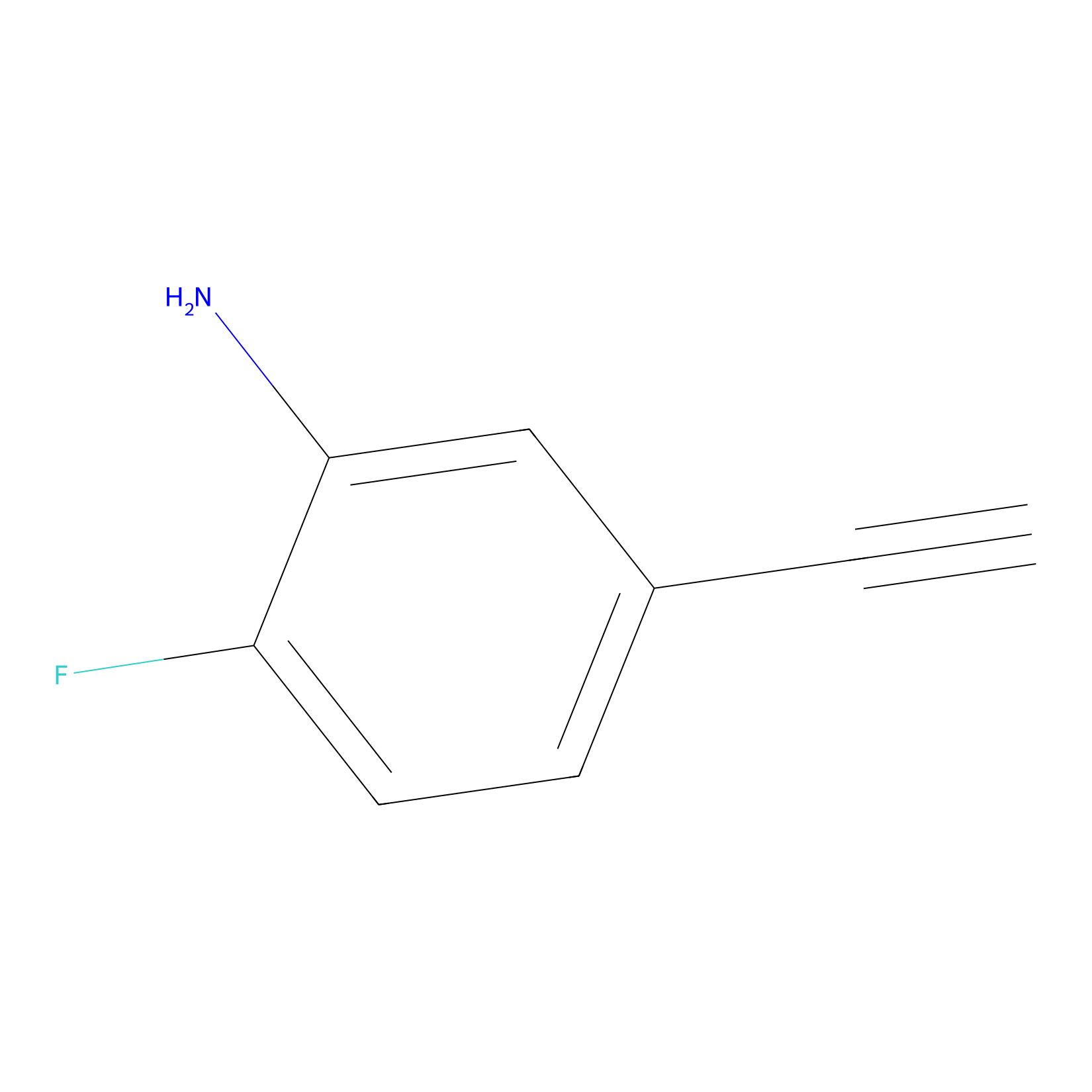 |
N.A. | LDD2235 | [4] | |
|
m-APA Probe Info |
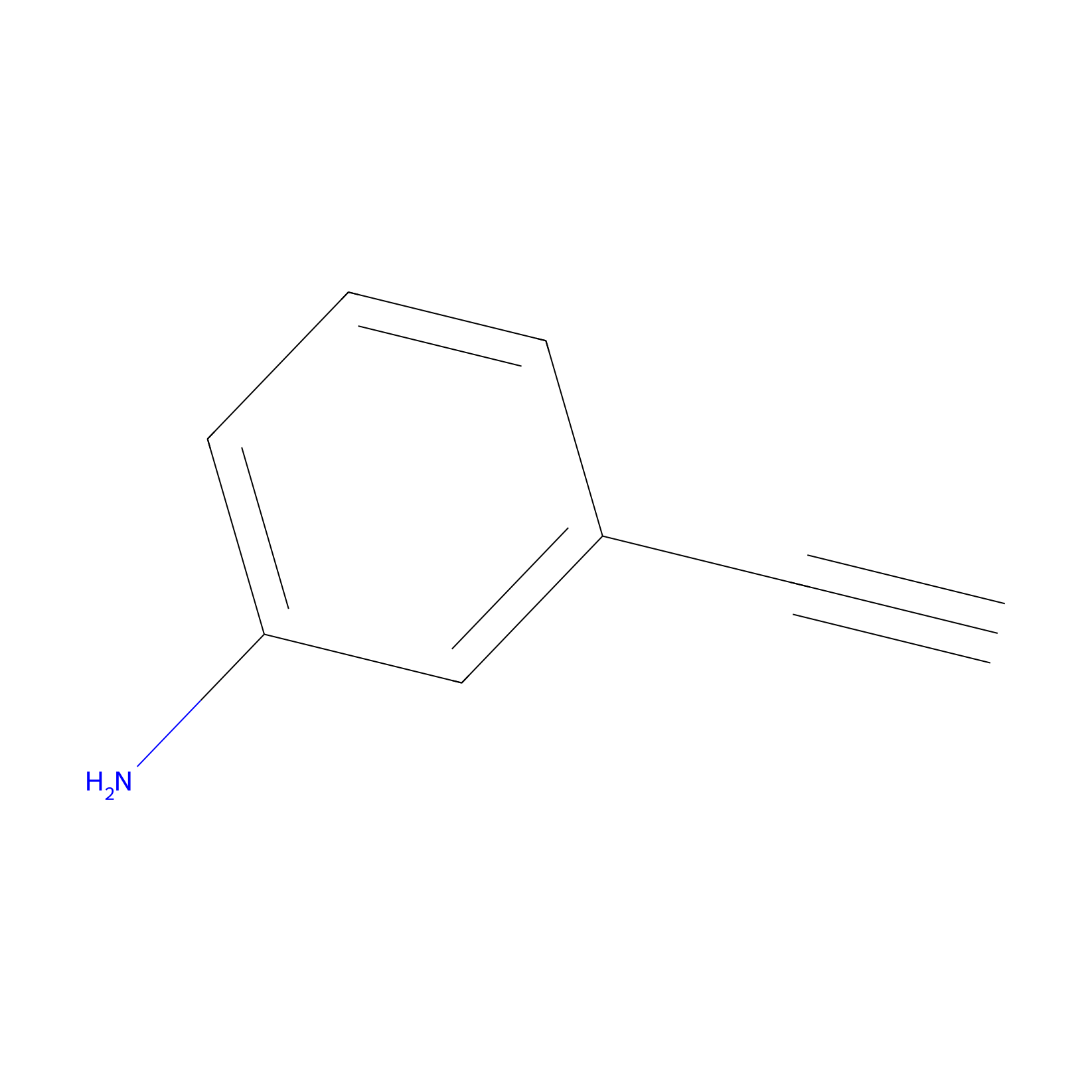 |
N.A. | LDD2231 | [4] | |
PAL-AfBPP Probe
| Probe name | Structure | Binding Site(Ratio) | Interaction ID | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
VE-P Probe Info |
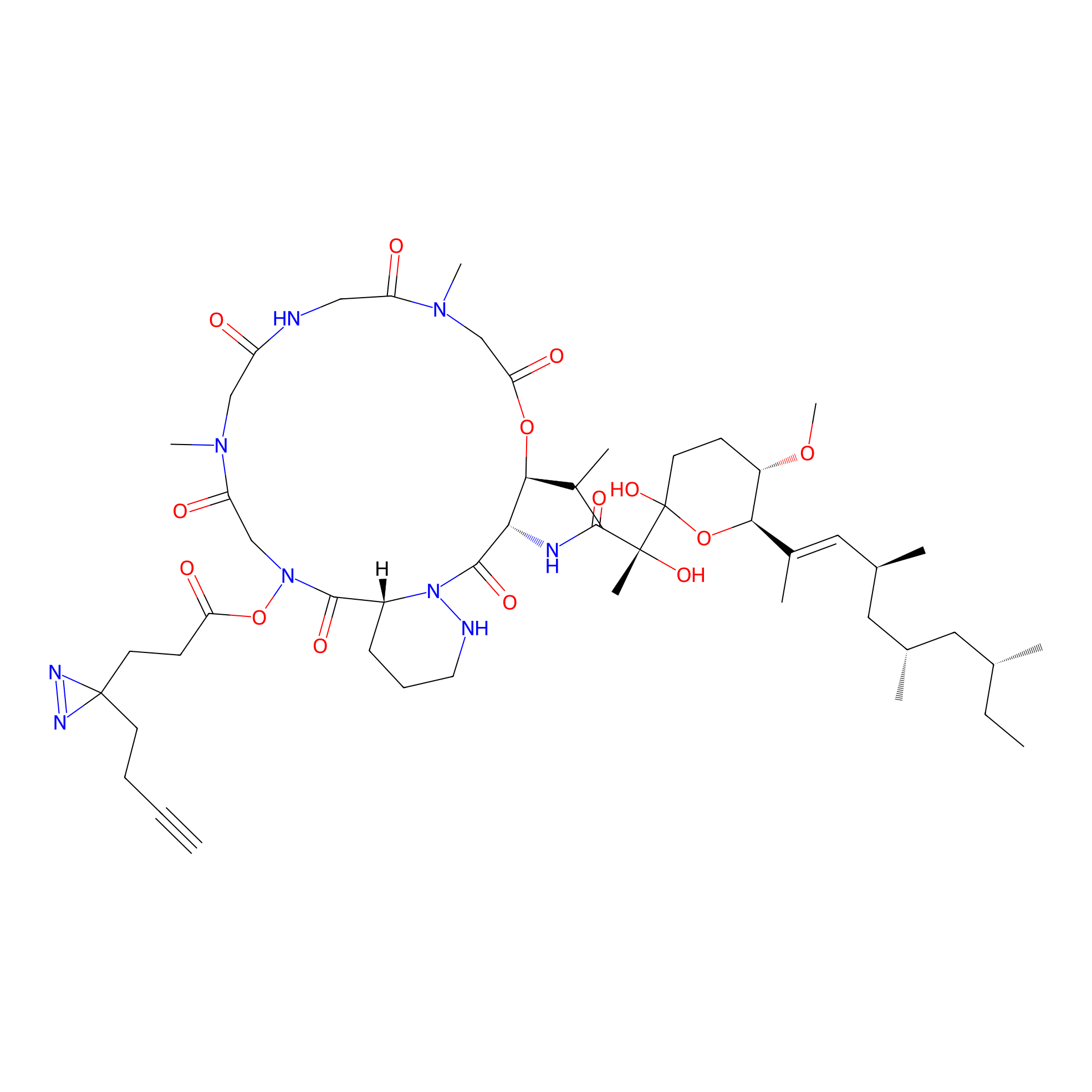 |
N.A. | LDD0396 | [5] | |
The Interaction Atlas With This Target
The Protein(s) Related To This Target
Enzyme
| Protein name | Family | Uniprot ID | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protein N-terminal glutamine amidohydrolase (NTAQ1) | NTAQ1 family | Q96HA8 | |||
Other
References
