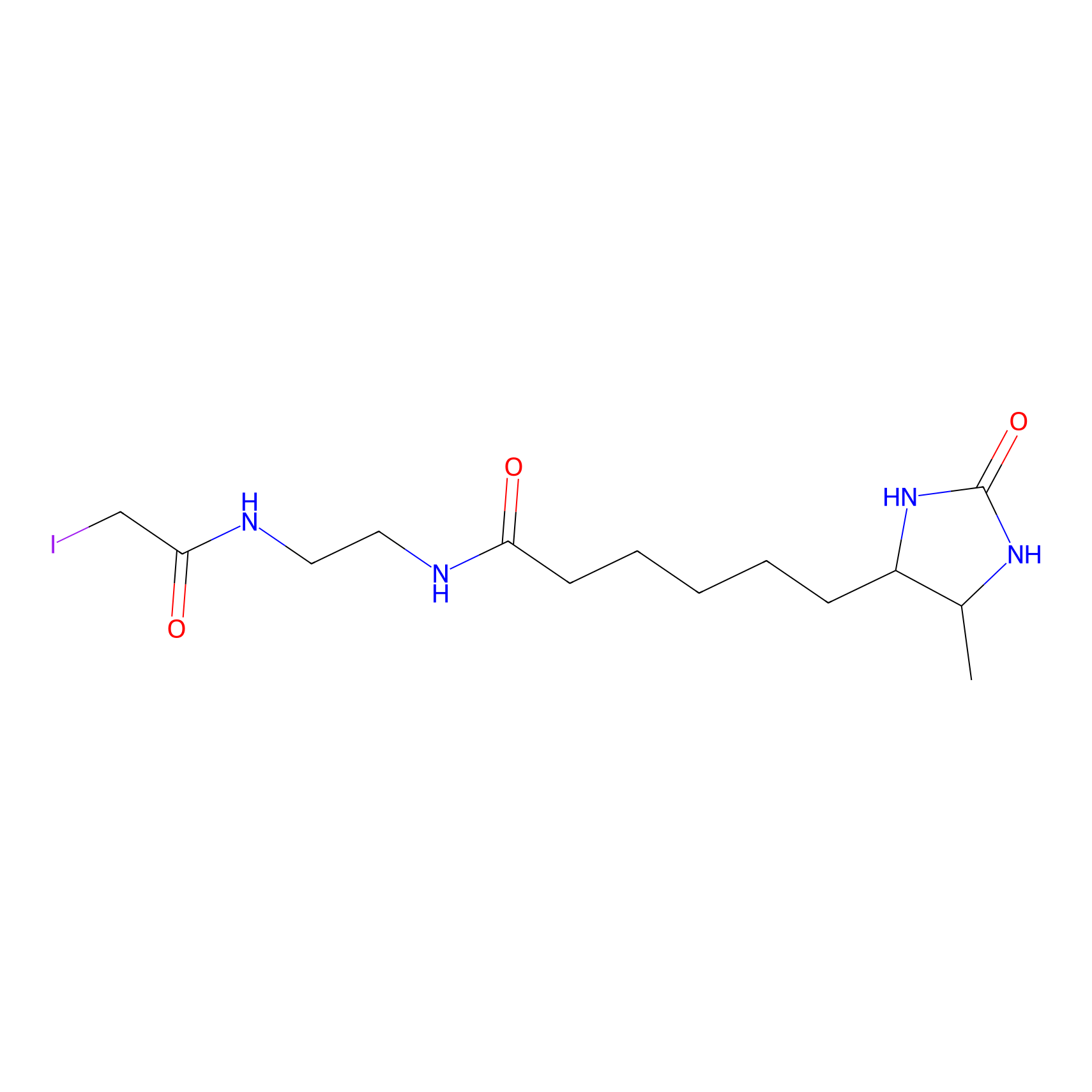
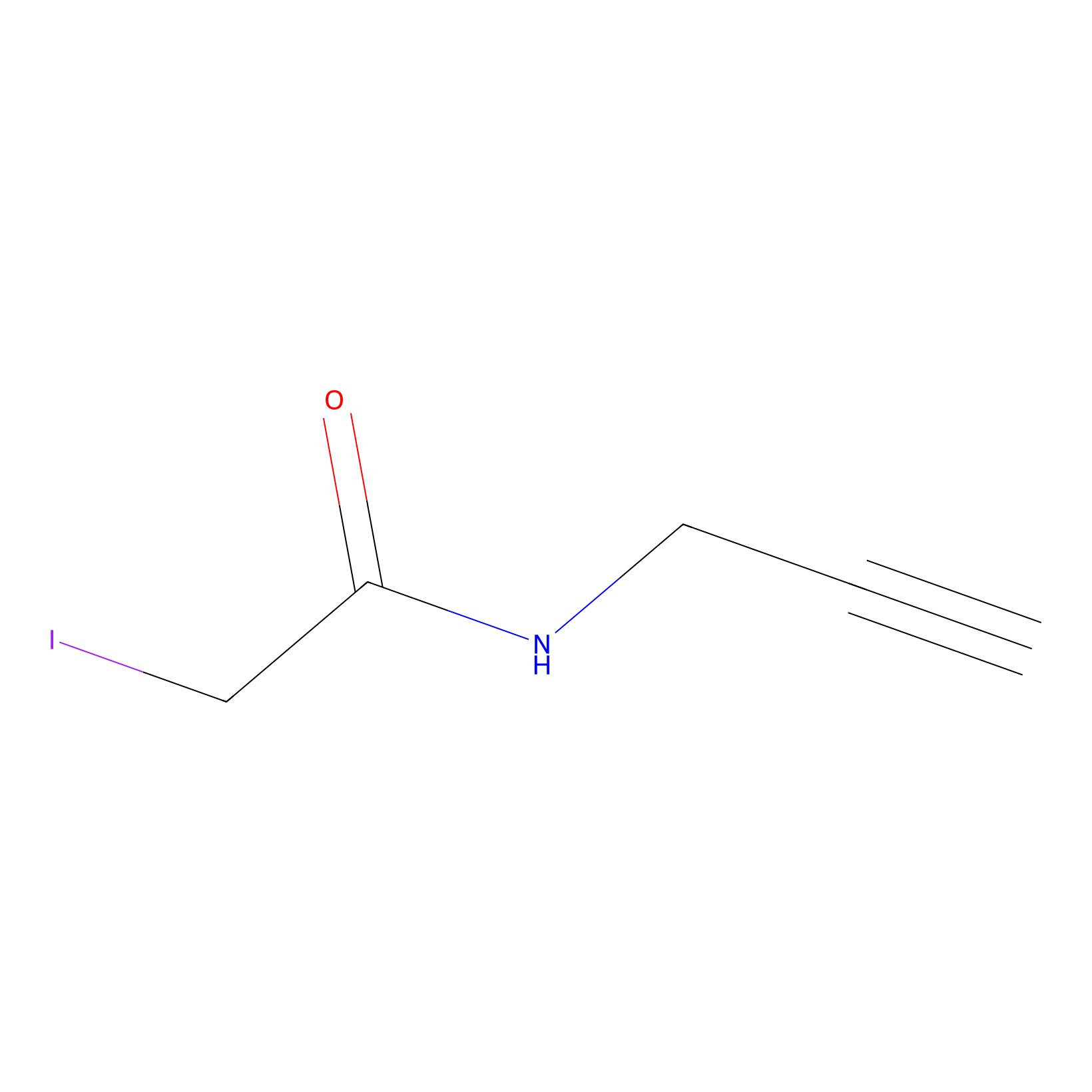
| Function |
Dioxygenase that plays a key role in active DNA demethylation, by catalyzing the sequential oxidation of the modified genomic base 5-methylcytosine (5mC) into 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC), 5-formylcytosine (5fC), and 5-carboxylcytosine (5caC). In addition to its role in DNA demethylation, plays a more general role in chromatin regulation by recruiting histone modifying protein complexes to alter histone marks and chromatin accessibility, leading to both activation and repression of gene expression. Plays therefore a role in many biological processes, including stem cell maintenance, T- and B-cell development, inflammation regulation, genomic imprinting, neural activity or DNA repair. Involved in the balance between pluripotency and lineage commitment of cells and plays a role in embryonic stem cells maintenance and inner cell mass cell specification. Together with QSER1, plays an essential role in the protection and maintenance of transcriptional and developmental programs to inhibit the binding of DNMT3A/3B and therefore de novo methylation. May play a role in pancreatic beta-cell specification during development. In this context, may function as an upstream epigenetic regulator of PAX4 presumably through direct recruitment by FOXA2 to a PAX4 enhancer to preserve its unmethylated status, thereby potentiating PAX4 expression to adopt beta-cell fate during endocrine lineage commitment. Under DNA hypomethylation conditions, such as in female meiotic germ cells, may induce epigenetic reprogramming of pericentromeric heterochromatin (PCH), the constitutive heterochromatin of pericentromeric regions. PCH forms chromocenters in the interphase nucleus and chromocenters cluster at the prophase of meiosis. In this context, may also be essential for chromocenter clustering in a catalytic activity-independent manner, possibly through the recruitment polycomb repressive complex 1 (PRC1) to the chromocenters. During embryonic development, may be required for normal meiotic progression in oocytes and meiotic gene activation. Binds preferentially to DNA containing cytidine-phosphate-guanosine (CpG) dinucleotides over CpH (H=A, T, and C), hemimethylated-CpG and hemimethylated-hydroxymethyl-CpG.; [Isoform 1]: Dioxygenase that plays a key role in active DNA demethylation. Binds to promoters, particularly to those with high CG content. In hippocampal neurons, isoform 1 regulates the expression of a unique subset of genes compared to isoform 2, although some overlap exists between both isoforms, hence differentially regulates excitatory synaptic transmission. In hippocampal neuron cell cultures, isoform 1 controls both miniature excitatory postsynaptic current amplitude and frequency. Isoform 1 may regulate genes involved in hippocampal-dependent memory, leading to positive regulation of memory, contrary to isoform 2 that may decrease memory.; [Isoform 2]: Dioxygenase that plays a key role in active DNA demethylation. As isoform 1, binds to promoters, particularly to those with high CG content, however displays reduced global chromatin affinity compared with isoform 1, leading to decreased global DNA demethylation compared with isoform 1. Contrary to isoform 1, isoform 2 localizes during S phase to sites of ongoing DNA replication in heterochromatin, causing a significant de novo 5hmC formation, globally, and more so in heterochromatin, including LINE 1 interspersed DNA repeats leading to their activation. In hippocampal neurons, isoform 2 regulates the expression of a unique subset of genes compared to isoform 1, although some overlap between both isoforms, hence differentially regulates excitatory synaptic transmission. In hippocampal neuron cell cultures, isoform 2 controls miniature excitatory postsynaptic current frequency, but not amplitude. Isoform 2 may regulate genes involved in hippocampal-dependent memory, leading to negative regulation of memory, contrary to isoform 1 that may improve memory. In immature and partially differentiated gonadotrope cells, directly represses luteinizing hormone gene LHB expression and does not catalyze 5hmC at the gene promoter.
|