Details of the Target
General Information of Target
| Target ID | LDTP12373 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Name | Inward rectifier potassium channel 16 (KCNJ16) | |||||
| Gene Name | KCNJ16 | |||||
| Gene ID | 3773 | |||||
| Synonyms |
Inward rectifier potassium channel 16; Inward rectifier K(+) channel Kir5.1; Potassium channel, inwardly rectifying subfamily J member 16 |
|||||
| 3D Structure | ||||||
| Sequence |
MESLLQHLDRFSELLAVSSTTYVSTWDPATVRRALQWARYLRHIHRRFGRHGPIRTALER
RLHNQWRQEGGFGRGPVPGLANFQALGHCDVLLSLRLLENRALGDAARYHLVQQLFPGPG VRDADEETLQESLARLARRRSAVHMLRFNGYRENPNLQEDSLMKTQAELLLERLQEVGKA EAERPARFLSSLWERLPQNNFLKVIAVALLQPPLSRRPQEELEPGIHKSPGEGSQVLVHW LLGNSEVFAAFCRALPAGLLTLVTSRHPALSPVYLGLLTDWGQRLHYDLQKGIWVGTESQ DVPWEELHNRFQSLCQAPPPLKDKVLTALETCKAQDGDFEVPGLSIWTDLLLALRSGAFR KRQVLGLSAGLSSV |
|||||
| Target Bioclass |
Transporter and channel
|
|||||
| Family |
Inward rectifier-type potassium channel (TC 1.A.2.1) family, KCNJ16 subfamily
|
|||||
| Subcellular location |
Membrane
|
|||||
| Function |
Inward rectifier potassium channels are characterized by a greater tendency to allow potassium to flow into the cell rather than out of it. Their voltage dependence is regulated by the concentration of extracellular potassium; as external potassium is raised, the voltage range of the channel opening shifts to more positive voltages. The inward rectification is mainly due to the blockage of outward current by internal magnesium. KCNJ16 may be involved in the regulation of fluid and pH balance. In the kidney, together with KCNJ10, mediates basolateral K(+) recycling in distal tubules; this process is critical for Na(+) reabsorption at the tubules.
|
|||||
| Uniprot ID | ||||||
| Ensemble ID | ||||||
| HGNC ID | ||||||
Probe(s) Labeling This Target
ABPP Probe
| Probe name | Structure | Binding Site(Ratio) | Interaction ID | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
IA-alkyne Probe Info |
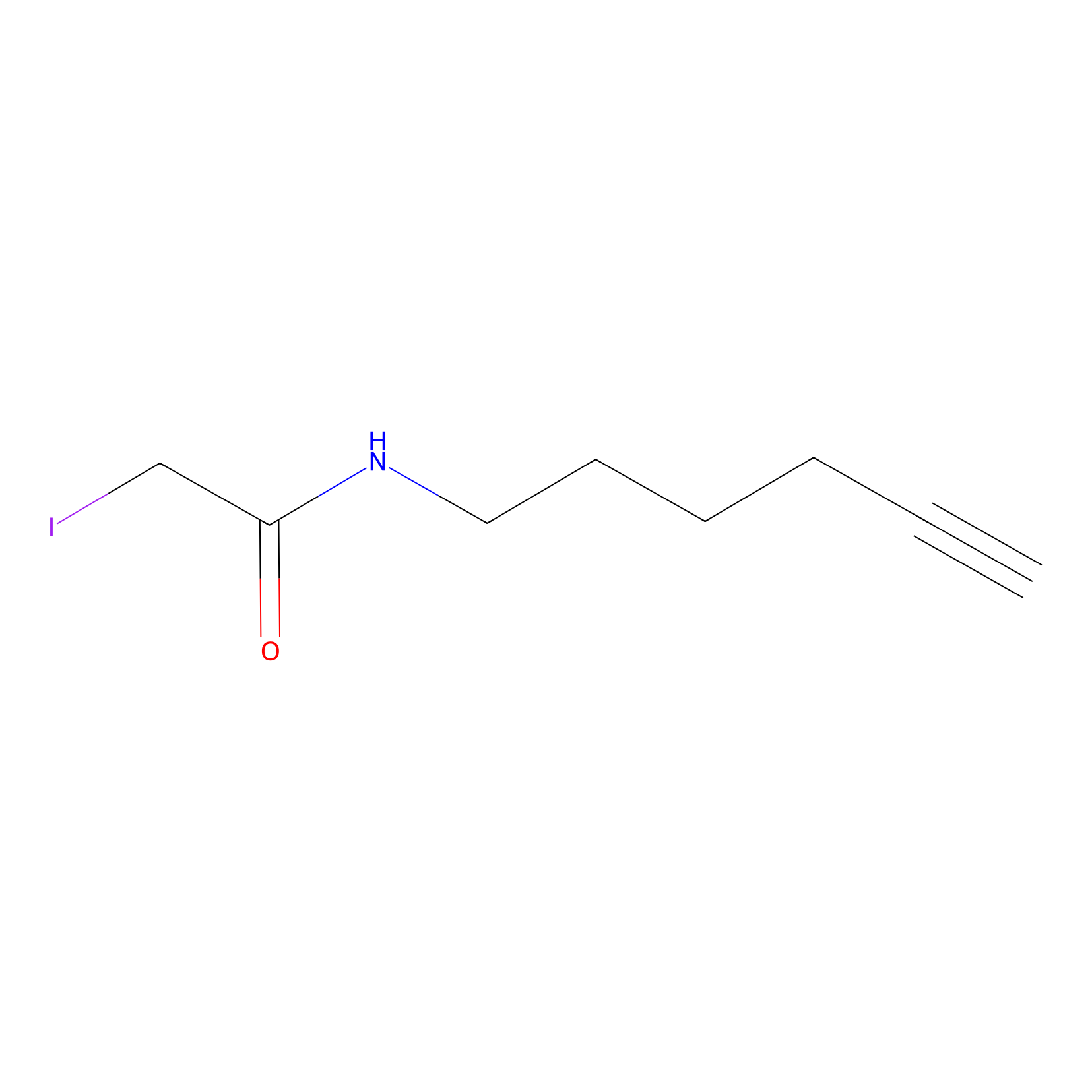 |
C43(3.81) | LDD2157 | [1] | |
|
DBIA Probe Info |
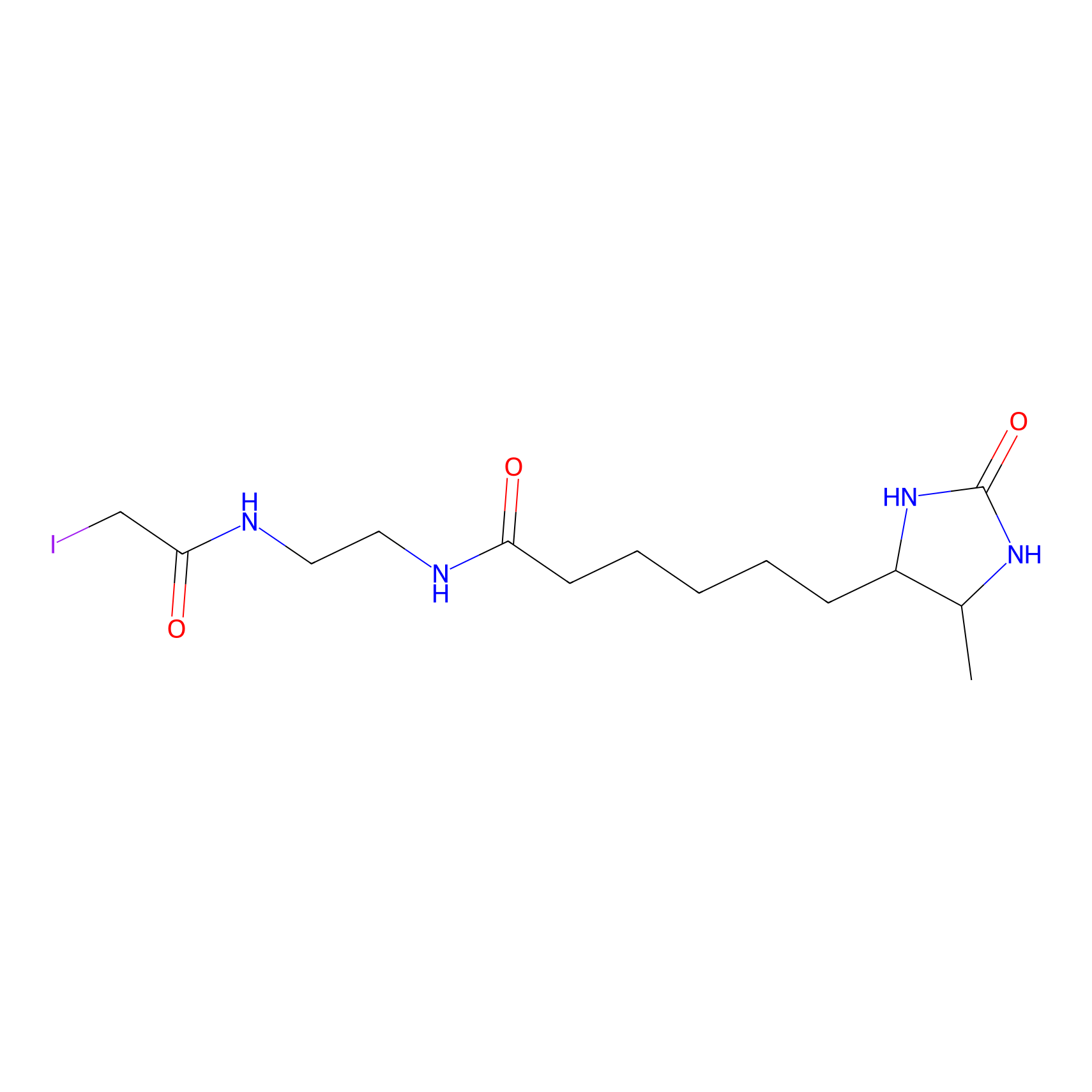 |
C363(1.75) | LDD3478 | [2] | |
Competitor(s) Related to This Target
References
