Details of the Target
General Information of Target
| Target ID | LDTP10154 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Name | ATP-dependent RNA helicase DHX58 (DHX58) | |||||
| Gene Name | DHX58 | |||||
| Gene ID | 79132 | |||||
| Synonyms |
D11LGP2E; LGP2; ATP-dependent RNA helicase DHX58; EC 3.6.4.13; ATP-dependent helicase LGP2; Protein D11Lgp2 homolog; RIG-I-like receptor 3; RLR-3; RIG-I-like receptor LGP2; RLR |
|||||
| 3D Structure | ||||||
| Sequence |
MAEFSQKRGKRRSDEGLGSMVDFLLANARLVLGVGGAAVLGIATLAVKRFIDRATSPRDE
DDTKADSWKELSLLKATPHLQPRPPPAALSQPVLPLAPSSSAPEGPAETDPEVTPQLSSP APLCLTLQERLLAFERDRVTIPAAQVALAKQLAGDIALELQAYFRSKFPELPFGAFVPGG PLYDGLQAGAADHVRLLVPLVLEPGLWSLVPGVDTVARDPRCWAVRRTQLEFCPRGSSPW DRFLVGGYLSSRVLLELLRKALAASVNWPAIGSLLGCLIRPSMASEELLLEVQHERLELT VAVLVAVPGVDADDRLLLAWPLEGLAGNLWLQDLYPVEAARLRALDDHDAGTRRRLLLLL CAVCRGCSALGQLGRGHLTQVVLRLGEDNVDWTEEALGERFLQALELLIGSLEQASLPCH FNPSVNLFSSLREEEIDDIGYALYSGLQEPEGLL |
|||||
| Target Bioclass |
Enzyme
|
|||||
| Family |
Helicase family, RLR subfamily
|
|||||
| Subcellular location |
Cytoplasm
|
|||||
| Function |
Acts as a regulator of RIGI and IFIH1/MDA5 mediated antiviral signaling. Cannot initiate antiviral signaling as it lacks the CARD domain required for activating MAVS/IPS1-dependent signaling events. Can have both negative and positive regulatory functions related to RIGI and IFIH1/MDA5 signaling and this role in regulating signaling may be complex and could probably depend on characteristics of the infecting virus or target cells, or both. Its inhibitory action on RIG-I signaling may involve the following mechanisms: competition with RIGI for binding to the viral RNA, binding to RIGI and inhibiting its dimerization and interaction with MAVS/IPS1, competing with IKBKE in its binding to MAVS/IPS1 thereby inhibiting activation of interferon regulatory factor 3 (IRF3). Its positive regulatory role may involve unwinding or stripping nucleoproteins of viral RNA thereby facilitating their recognition by RIGI and IFIH1/MDA5. Involved in the innate immune response to various RNA viruses and some DNA viruses such as poxviruses and coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, and also to the bacterial pathogen Listeria monocytogenes. Can bind both ssRNA and dsRNA, with a higher affinity for dsRNA. Shows a preference to 5'-triphosphorylated RNA, although it can recognize RNA lacking a 5'-triphosphate.
|
|||||
| Uniprot ID | ||||||
| Ensemble ID | ||||||
| HGNC ID | ||||||
Probe(s) Labeling This Target
ABPP Probe
| Probe name | Structure | Binding Site(Ratio) | Interaction ID | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
DBIA Probe Info |
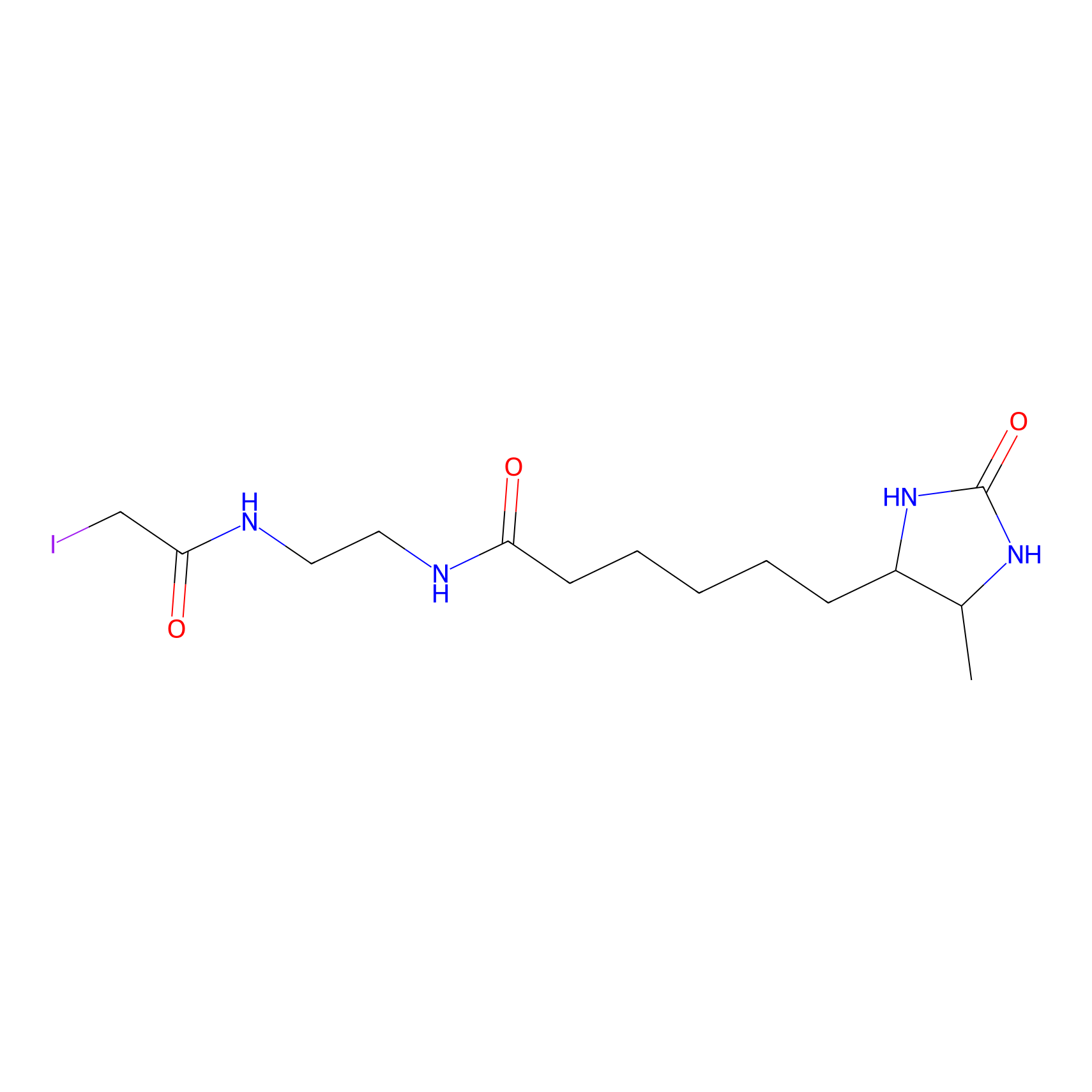 |
C221(1.91) | LDD3325 | [1] | |
|
IA-alkyne Probe Info |
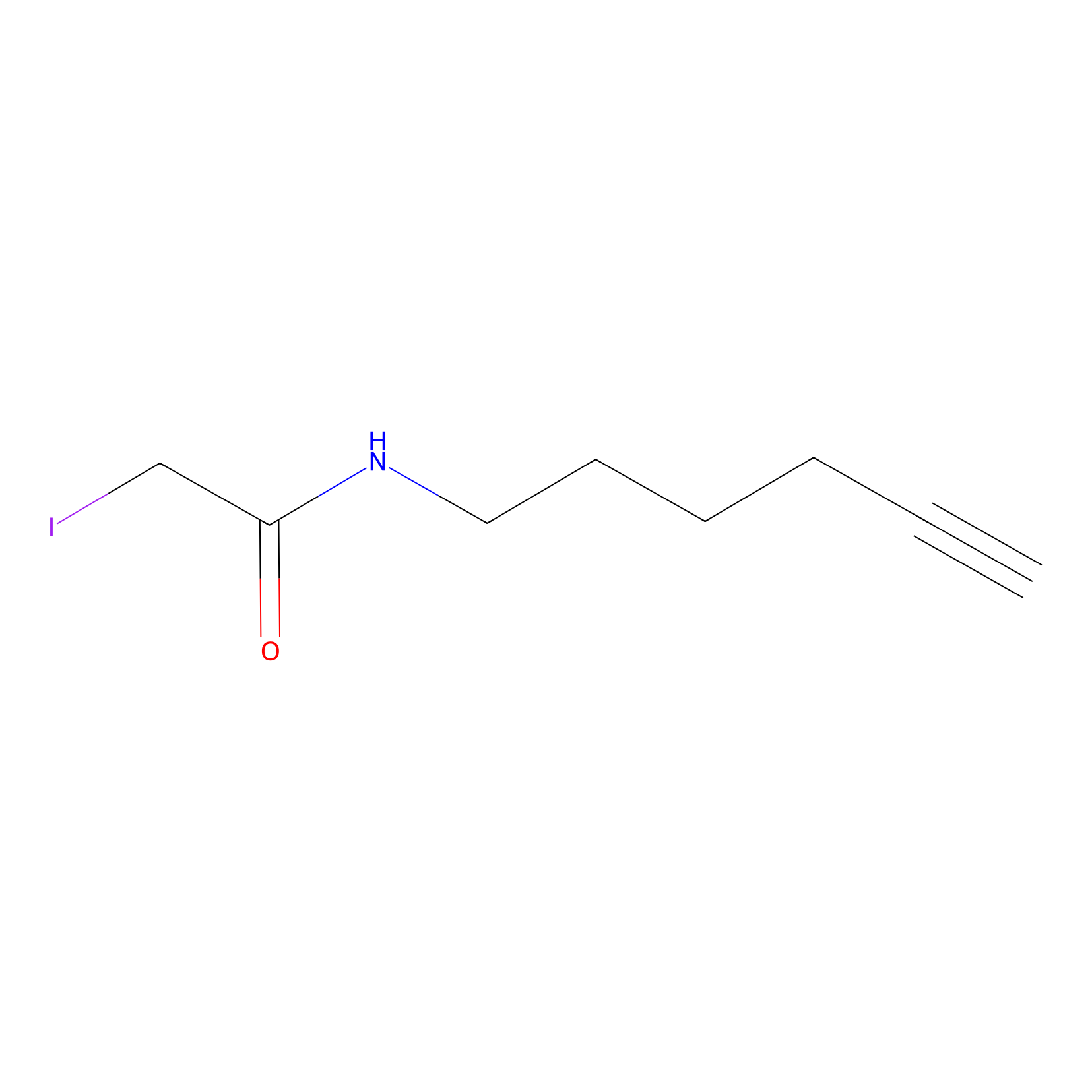 |
C322(15.48) | LDD1703 | [2] | |
Competitor(s) Related to This Target
The Interaction Atlas With This Target
The Protein(s) Related To This Target
Enzyme
Transcription factor
| Protein name | Family | Uniprot ID | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gamma-interferon-inducible protein 16 (IFI16) | HIN-200 family | Q16666 | |||
| NF-kappa-B-repressing factor (NKRF) | . | O15226 | |||
Other
| Protein name | Family | Uniprot ID | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 6 (EIF6) | EIF-6 family | P56537 | |||
| Double-stranded RNA-binding protein Staufen homolog 2 (STAU2) | . | Q9NUL3 | |||
References
