Details of the Target
General Information of Target
| Target ID | LDTP06741 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Name | HLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DR beta 5 chain (HLA-DRB5) | |||||
| Gene Name | HLA-DRB5 | |||||
| Gene ID | 3127 | |||||
| Synonyms |
HLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DR beta 5 chain; DR beta-5; DR2-beta-2; Dw2; MHC class II antigen DRB5 |
|||||
| 3D Structure | ||||||
| Sequence |
MVCLKLPGGSYMAKLTVTLMVLSSPLALAGDTRPRFLQQDKYECHFFNGTERVRFLHRDI
YNQEEDLRFDSDVGEYRAVTELGRPDAEYWNSQKDFLEDRRAAVDTYCRHNYGVGESFTV QRRVEPKVTVYPARTQTLQHHNLLVCSVNGFYPGSIEVRWFRNSQEEKAGVVSTGLIQNG DWTFQTLVMLETVPRSGEVYTCQVEHPSVTSPLTVEWRAQSESAQSKMLSGVGGFVLGLL FLGAGLFIYFKNQKGHSGLHPTGLVS |
|||||
| Target Bioclass |
Immunoglobulin
|
|||||
| Family |
MHC class II family
|
|||||
| Subcellular location |
Cell membrane
|
|||||
| Function |
Binds peptides derived from antigens that access the endocytic route of antigen presenting cells (APC) and presents them on the cell surface for recognition by the CD4 T-cells. The peptide binding cleft accommodates peptides of 10-30 residues. The peptides presented by MHC class II molecules are generated mostly by degradation of proteins that access the endocytic route, where they are processed by lysosomal proteases and other hydrolases. Exogenous antigens that have been endocytosed by the APC are thus readily available for presentation via MHC II molecules, and for this reason this antigen presentation pathway is usually referred to as exogenous. As membrane proteins on their way to degradation in lysosomes as part of their normal turn-over are also contained in the endosomal/lysosomal compartments, exogenous antigens must compete with those derived from endogenous components. Autophagy is also a source of endogenous peptides, autophagosomes constitutively fuse with MHC class II loading compartments. In addition to APCs, other cells of the gastrointestinal tract, such as epithelial cells, express MHC class II molecules and CD74 and act as APCs, which is an unusual trait of the GI tract. To produce a MHC class II molecule that presents an antigen, three MHC class II molecules (heterodimers of an alpha and a beta chain) associate with a CD74 trimer in the ER to form a heterononamer. Soon after the entry of this complex into the endosomal/lysosomal system where antigen processing occurs, CD74 undergoes a sequential degradation by various proteases, including CTSS and CTSL, leaving a small fragment termed CLIP (class-II-associated invariant chain peptide). The removal of CLIP is facilitated by HLA-DM via direct binding to the alpha-beta-CLIP complex so that CLIP is released. HLA-DM stabilizes MHC class II molecules until primary high affinity antigenic peptides are bound. The MHC II molecule bound to a peptide is then transported to the cell membrane surface. In B-cells, the interaction between HLA-DM and MHC class II molecules is regulated by HLA-DO. Primary dendritic cells (DCs) also to express HLA-DO. Lysosomal microenvironment has been implicated in the regulation of antigen loading into MHC II molecules, increased acidification produces increased proteolysis and efficient peptide loading.
|
|||||
| Uniprot ID | ||||||
| Ensemble ID | ||||||
| HGNC ID | ||||||
| ChEMBL ID | ||||||
Probe(s) Labeling This Target
ABPP Probe
| Probe name | Structure | Binding Site(Ratio) | Interaction ID | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
DBIA Probe Info |
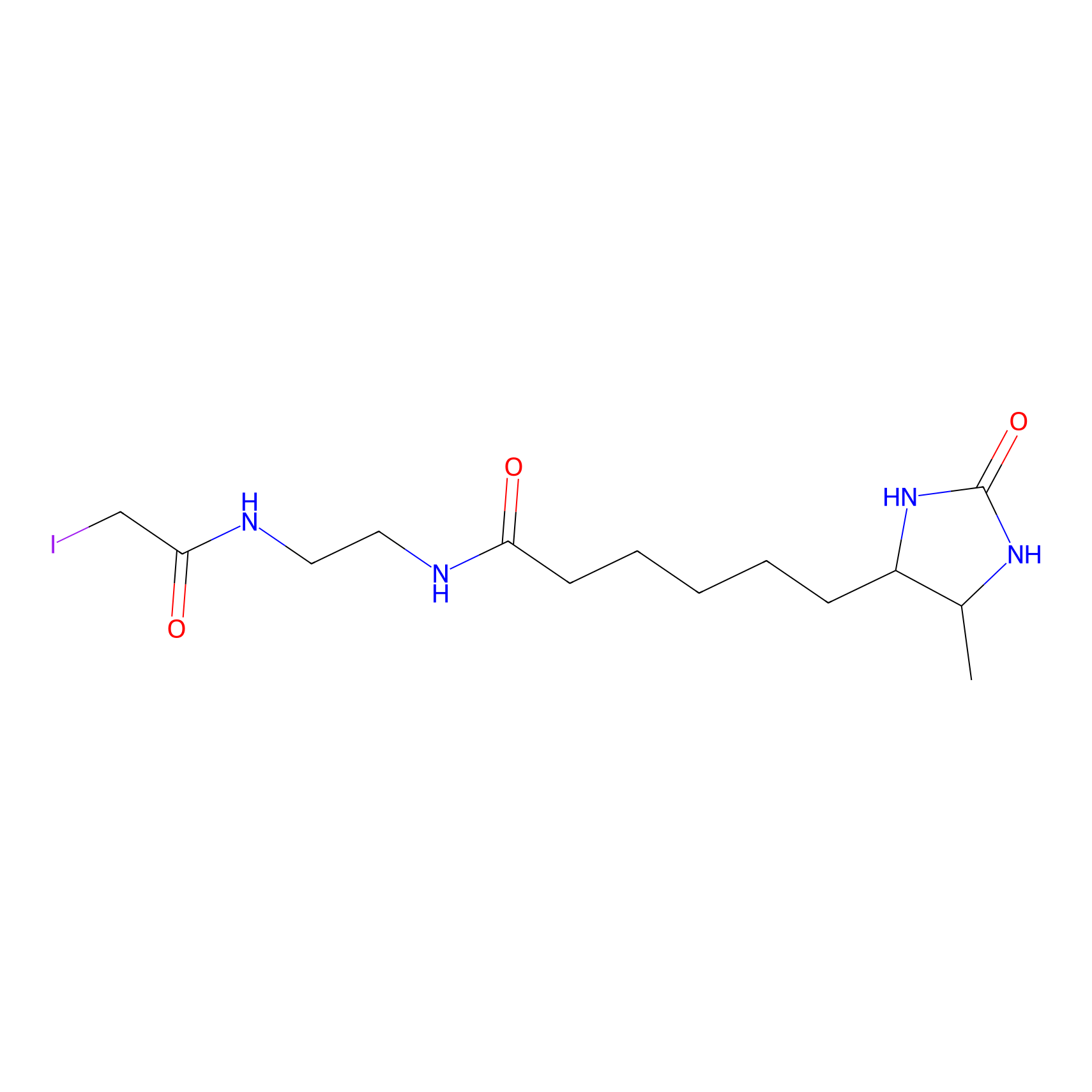 |
C108(1.68) | LDD3313 | [1] | |
Competitor(s) Related to This Target
