Details of the Target
General Information of Target
| Target ID | LDTP03740 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Name | Nuclear receptor ROR-alpha (RORA) | |||||
| Gene Name | RORA | |||||
| Gene ID | 6095 | |||||
| Synonyms |
NR1F1; RZRA; Nuclear receptor ROR-alpha; Nuclear receptor RZR-alpha; Nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group F member 1; RAR-related orphan receptor A; Retinoid-related orphan receptor-alpha |
|||||
| 3D Structure | ||||||
| Sequence |
MESAPAAPDPAASEPGSSGADAAAGSRETPLNQESARKSEPPAPVRRQSYSSTSRGISVT
KKTHTSQIEIIPCKICGDKSSGIHYGVITCEGCKGFFRRSQQSNATYSCPRQKNCLIDRT SRNRCQHCRLQKCLAVGMSRDAVKFGRMSKKQRDSLYAEVQKHRMQQQQRDHQQQPGEAE PLTPTYNISANGLTELHDDLSNYIDGHTPEGSKADSAVSSFYLDIQPSPDQSGLDINGIK PEPICDYTPASGFFPYCSFTNGETSPTVSMAELEHLAQNISKSHLETCQYLREELQQITW QTFLQEEIENYQNKQREVMWQLCAIKITEAIQYVVEFAKRIDGFMELCQNDQIVLLKAGS LEVVFIRMCRAFDSQNNTVYFDGKYASPDVFKSLGCEDFISFVFEFGKSLCSMHLTEDEI ALFSAFVLMSADRSWLQEKVKIEKLQQKIQLALQHVLQKNHREDGILTKLICKVSTLRAL CGRHTEKLMAFKAIYPDIVRLHFPPLYKELFTSEFEPAMQIDG |
|||||
| Target Type |
Preclinical
|
|||||
| Target Bioclass |
Transcription factor
|
|||||
| Family |
Nuclear hormone receptor family, NR1 subfamily
|
|||||
| Subcellular location |
Nucleus
|
|||||
| Function |
Nuclear receptor that binds DNA as a monomer to ROR response elements (RORE) containing a single core motif half-site 5'-AGGTCA-3' preceded by a short A-T-rich sequence. Key regulator of embryonic development, cellular differentiation, immunity, circadian rhythm as well as lipid, steroid, xenobiotics and glucose metabolism. Considered to have intrinsic transcriptional activity, have some natural ligands like oxysterols that act as agonists (25-hydroxycholesterol) or inverse agonists (7-oxygenated sterols), enhancing or repressing the transcriptional activity, respectively. Recruits distinct combinations of cofactors to target genes regulatory regions to modulate their transcriptional expression, depending on the tissue, time and promoter contexts. Regulates genes involved in photoreceptor development including OPN1SW, OPN1SM and ARR3 and skeletal muscle development with MYOD1. Required for proper cerebellum development. Regulates SHH gene expression, among others, to induce granule cells proliferation as well as expression of genes involved in calcium-mediated signal transduction. Regulates the circadian expression of several clock genes, including CLOCK, BMAL1, NPAS2 and CRY1. Competes with NR1D1 for binding to their shared DNA response element on some clock genes such as BMAL1, CRY1 and NR1D1 itself, resulting in NR1D1-mediated repression or RORA-mediated activation of clock genes expression, leading to the circadian pattern of clock genes expression. Therefore influences the period length and stability of the clock. Regulates genes involved in lipid metabolism such as apolipoproteins APOA1, APOA5, APOC3 and PPARG. In liver, has specific and redundant functions with RORC as positive or negative modulator of expression of genes encoding phase I and phase II proteins involved in the metabolism of lipids, steroids and xenobiotics, such as CYP7B1 and SULT2A1. Induces a rhythmic expression of some of these genes. In addition, interplays functionally with NR1H2 and NR1H3 for the regulation of genes involved in cholesterol metabolism. Also involved in the regulation of hepatic glucose metabolism through the modulation of G6PC1 and PCK1. In adipose tissue, plays a role as negative regulator of adipocyte differentiation, probably acting through dual mechanisms. May suppress CEBPB-dependent adipogenesis through direct interaction and PPARG-dependent adipogenesis through competition for DNA-binding. Downstream of IL6 and TGFB and synergistically with RORC isoform 2, is implicated in the lineage specification of uncommitted CD4(+) T-helper (T(H)) cells into T(H)17 cells, antagonizing the T(H)1 program. Probably regulates IL17 and IL17F expression on T(H) by binding to the essential enhancer conserved non-coding sequence 2 (CNS2) in the IL17-IL17F locus. Involved in hypoxia signaling by interacting with and activating the transcriptional activity of HIF1A. May inhibit cell growth in response to cellular stress. May exert an anti-inflammatory role by inducing CHUK expression and inhibiting NF-kappa-B signaling.
|
|||||
| TTD ID | ||||||
| Uniprot ID | ||||||
| DrugMap ID | ||||||
| Ensemble ID | ||||||
| HGNC ID | ||||||
| ChEMBL ID | ||||||
Probe(s) Labeling This Target
ABPP Probe
| Probe name | Structure | Binding Site(Ratio) | Interaction ID | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
DBIA Probe Info |
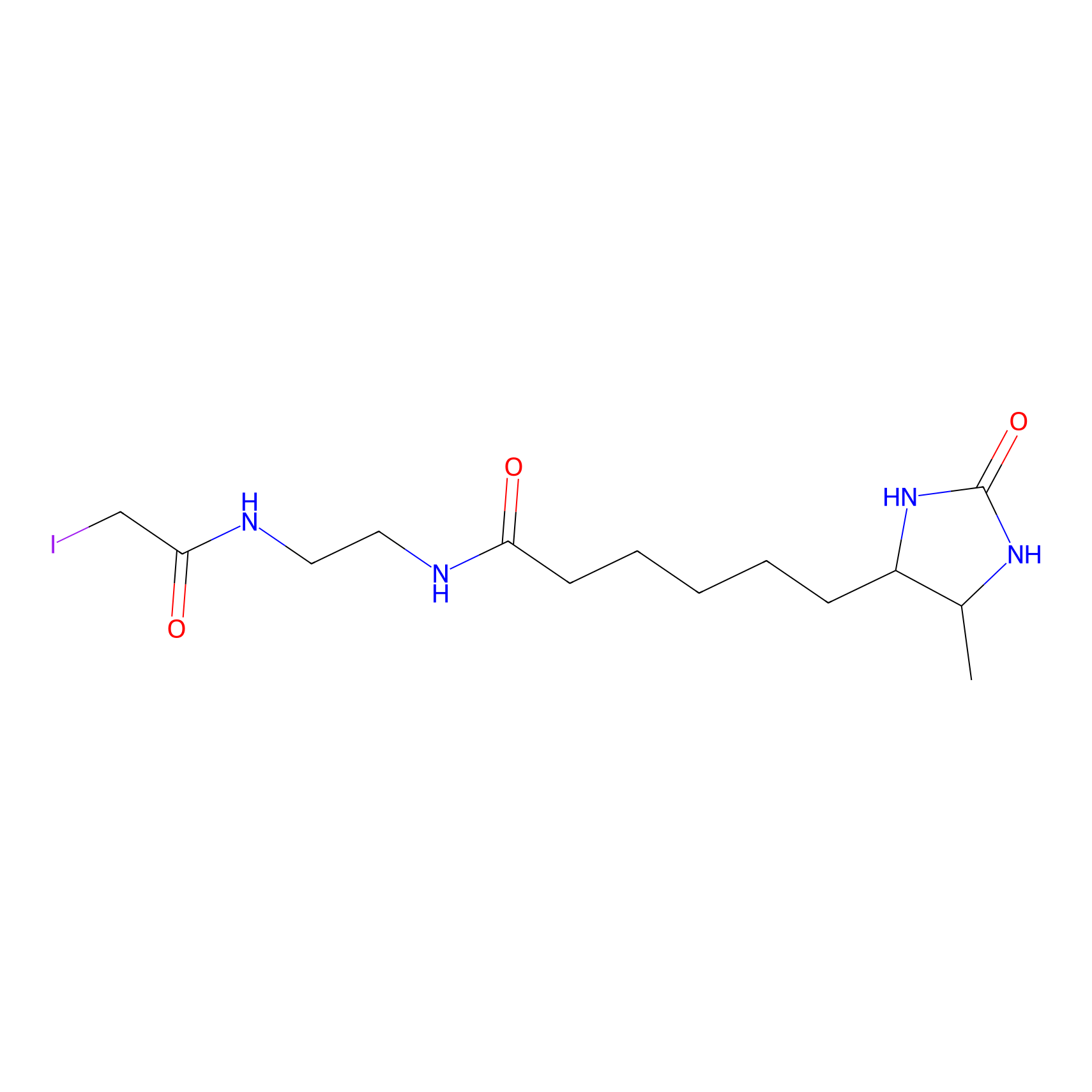 |
C54(1.60) | LDD2469 | [1] | |
Competitor(s) Related to This Target
