Details of the Target
General Information of Target
Probe(s) Labeling This Target
ABPP Probe
| Probe name | Structure | Binding Site(Ratio) | Interaction ID | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
DBIA Probe Info |
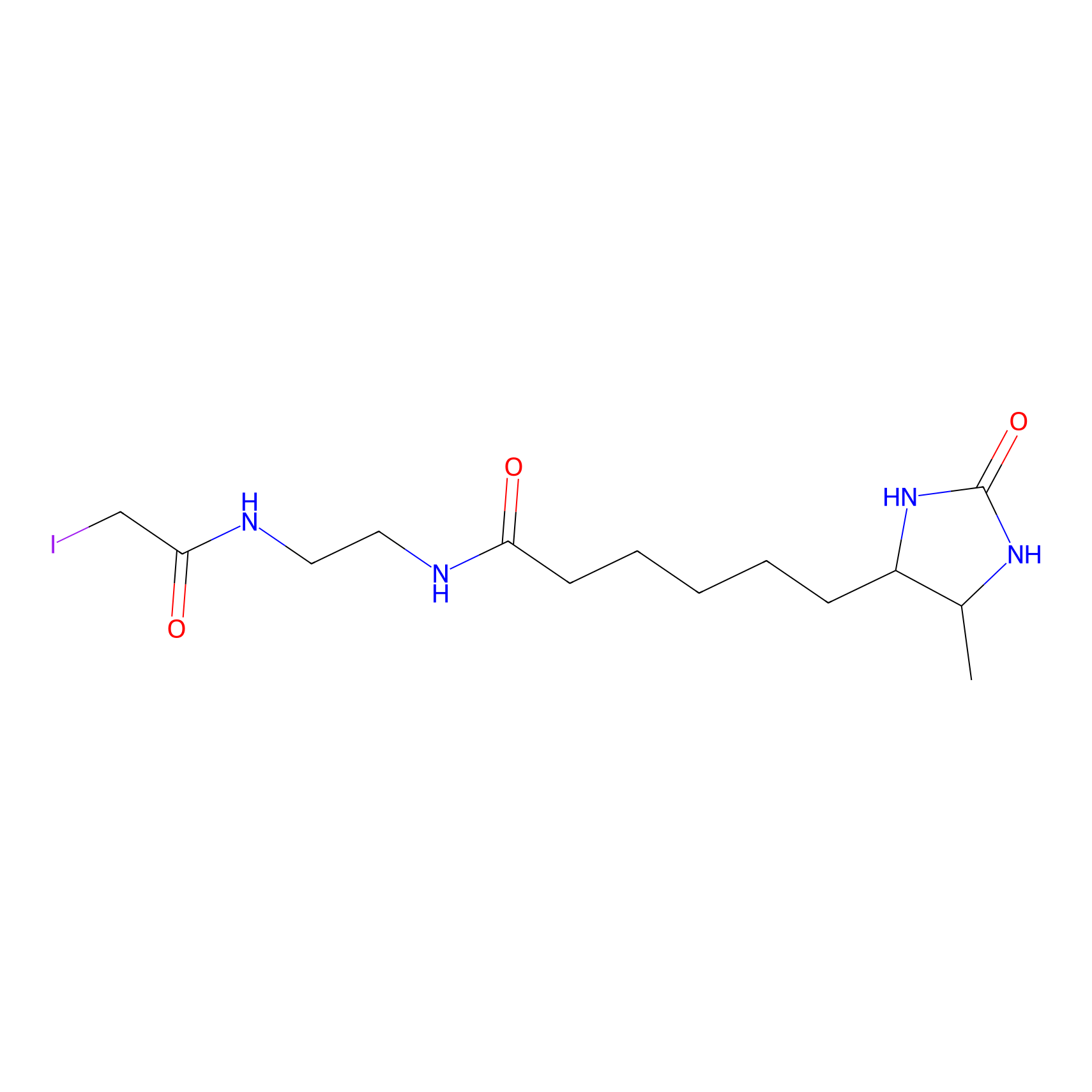 |
C117(4.13) | LDD2275 | [1] | |
Competitor(s) Related to This Target
